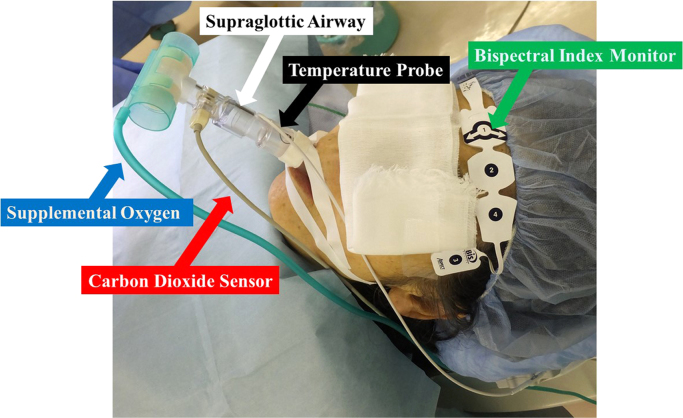
Fig. 1.
In a patient with a supraglottic airway (SGA) (white arrow), in who deep sedation was monitored by a bispectral index monitor (green arrow) pasted on the front of the forehead, radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation was performed under an intravenous administration of propofol and dexmedetomidine. Supplemental oxygen (blue arrow) was routinely used with a flow rate of 5–10 l per minute via an SGA with spontaneous breathing to maintain the peripheral oxygen saturation at more than 95%. The exhaling carbon dioxide sensor (red arrow) was attached to the SGA. A temperature probe to monitor the esophageal temperature (black arrow) was inserted through the nostril of the patient through a side hole of the SGA.