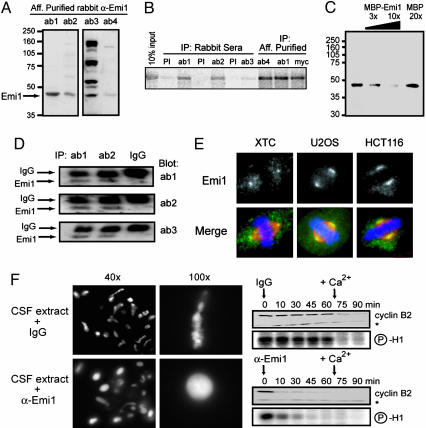
Fig. 1.
Characterization of anti-Emi1 antibodies. (A) A 44-kDa protein is recognized by affinity-purified anti-Emi1 antibodies in CSF-arrested eggs. CSF extract was immunoblotted with affinity-purified antibodies from four rabbits immunized against Emi1. (B) Anti-Emi1 antibodies immunoprecipitate expressed Emi1. IVT myc-Emi1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) by reactive sera and affinity-purified antibodies, but not by preimmune (PI) sera. (C) Emi1 antibody recognition of the 44-kDa species is blocked with antigen. CSF extract was blotted with affinity-purified antibody that was unblocked or blocked with increasing purified MBP-Emi1 fusion protein up to 10-fold molar excess over antibody or blocked with 20-fold molar excess of MBP protein over antibody. (D) Each of the anti-Emi1 antibodies detects the same 44-kDa protein. Immunoprecipitates from CSF extract with two anti-Emi1 antibodies or control IgG were immunoblotted with three anti-Emi1 antibodies. (E) Anti-Emi1 antibody detects conserved Emi1 localization to the spindle poles. Metaphase chromosomes, spindles, and Emi1 were visualized in Xenopus somatic XTC cells, human U2OS cells, and human HCT116 cells by fluorescence microscopy. The merged images show DNA (blue), α-tubulin (red), and Emi1 (green). (Magnification: ×63.) (F) Addition of anti-Emi1 antibody to CSF extract induces chromatin decondensation, MPF inactivation, and cyclin B destruction without calcium addition. CSF extract was supplemented with CHX and sperm and treated with anti-Emi1 antibodies or control IgG. After 60 min, sperm chromatin was stained with Hoechst and visualized by epifluorescence microscopy. Similar extract was incubated with anti-Emi1 antibodies or IgG and incubated for 60 min before addition of calcium to trigger MII exit. Time points were processed for histone H1 kinase activity and immunoblot analysis. A nonspecific band (*) recognized by the anti-cyclin B2 antibody serves as a loading control.