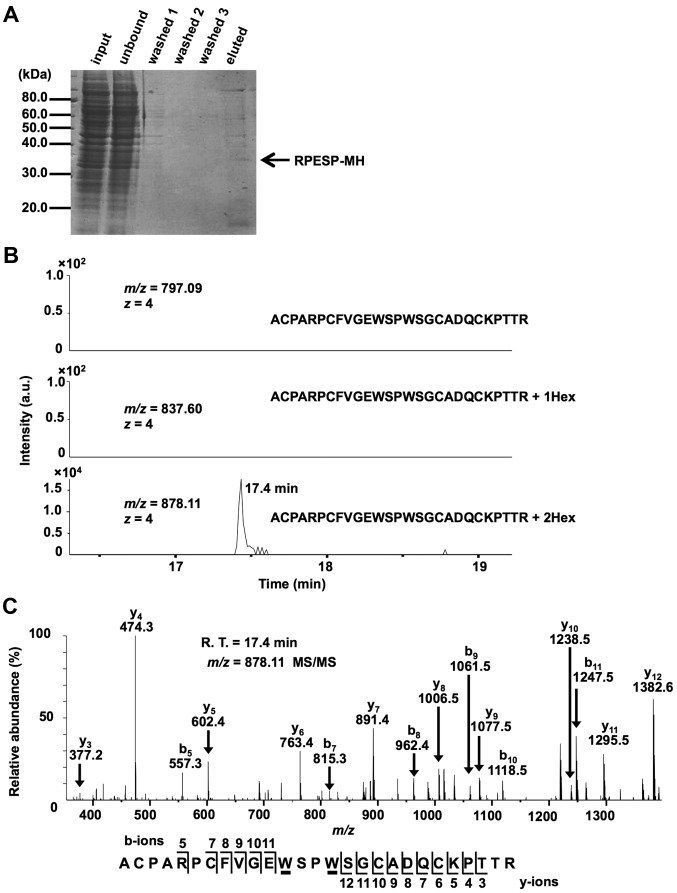
Figure 2.
RPESP is C-mannosylated in cells. (A) Purification of recombinant RPESP-MH from whole-cell lysate of HT1080-RPESP-MH. HT1080-RPESP-MH cells were lysed and cell lysate was treated with ammonium sulfate. The precipitate between 30–60% saturation of ammonium sulfate was dissolved in PBS (input) and recombinant RPESP-MH was purified using Ni-NTA agarose. These samples were electrophoresed and detected by CBB staining. (B and C) Determination of C-mannosylation sites within RPESP. The samples were digested with trypsin and the resulting peptides were analyzed using the targeted MS/MS method. According to the inclusion list of three quadruple-protonated parent ions of un-mannosylated (m/z, 797.09), mono-mannosylated (m/z, 837.60) and di-mannosylated 69ACPARPCFVGEWSPWSGCADQCKPTTR95 peptides (m/z, 878.11), MS/MS spectra were obtained. Selected ion chromatograms of y5 ion (602.366±20 ppm) of these parent ions were determined (B). The MS/MS spectrum of the quadruple-charged di-mannosylated peptide ion (m/z, 878.11) is presented (C). The indicated b- and y-series ions were detected as singly charged ions and C-mannosylation at the W80 and W83 residues of RPESP were suggested. C-mannosyltryptophans are underlined. RPESP, RPE-spondin; CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue; MS, mass spectrometry; Hex, hexose; R.T., retention time.