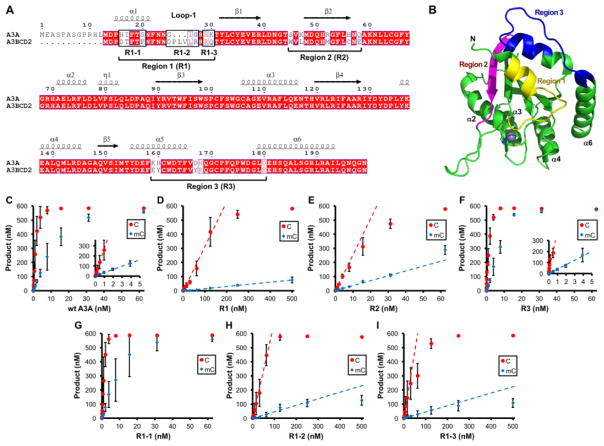
Figure 4. Identification of A3A regions important for deaminase activity and mC selectivity.
(A) Sequence alignment of A3A and A3B CD2. The three regions (Region 1–3) of A3A that show sequence differences with A3B CD2 are mutated to the amino acids of A3B CD2 to generate mutants R1, R2 and R3. (B) The three mutated regions (with distinct colors) are mapped onto A3A structure (5SWW) [75], in which the active center Zn and its coordinating histidine and cysteines are shown as a sphere and sticks, respectively. Only region 1 (loop-1 region) is next to the Zn-active center. Region 2 is on the opposite end of the active center, and region 3 is on loop 10 that is also far away from the active center. (C–I) Dose dependent activity assay for C and mC deamination for wt A3A and the six A3A mutants (R1, R2, R3, R1-1, R1-2, R1-3) shown in panel-A. Dose response deaminase assays were performed as described in Fig. 3 legends. S.D. was estimated from data collected in three independent experiments.