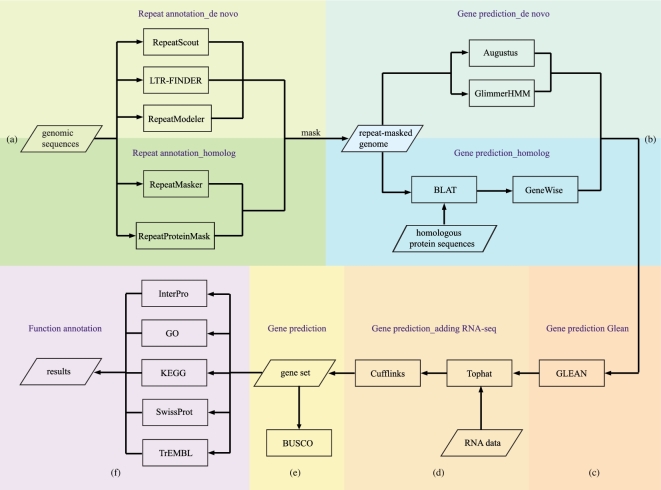
Figure 2:
An overview of the annotation workflow. The workflow begins with assembled genomic sequences, and it produces results of the repeat annotation, protein-coding gene prediction, and functional annotation. (a) Repeat annotation: repeats in the genome are detected in two different methods: de novo and homolog based. In the de novo method, RepeatScout, LTR-FINDER, and RepeatModeler are used to build de novo repeat libraries and further classified by RepeatMasker. In the homolog-based method, RepeatMasker and RepeatProteinMask are performed to search TEs by aligning sequences against existing libraries. (b) Gene prediction: before the gene prediction, TEs are totally masked. Augustus and GlimmerHMM are used to perform de novo prediction; BLAT and GeneWise are executed to predict gene models based on homologous protein sequences. (c) GLEAN is performed to obtain a consensus gene set. (d) In combination with the clean RNA sequenced reads, a more comprehensive gene set is integrated finally. (e) Estimation of the completeness of the gene set using BUSCO. (f) Functional annotation.