Figure 7. EA-mediated sympathetic stimulation induces MSC release into the circulation.
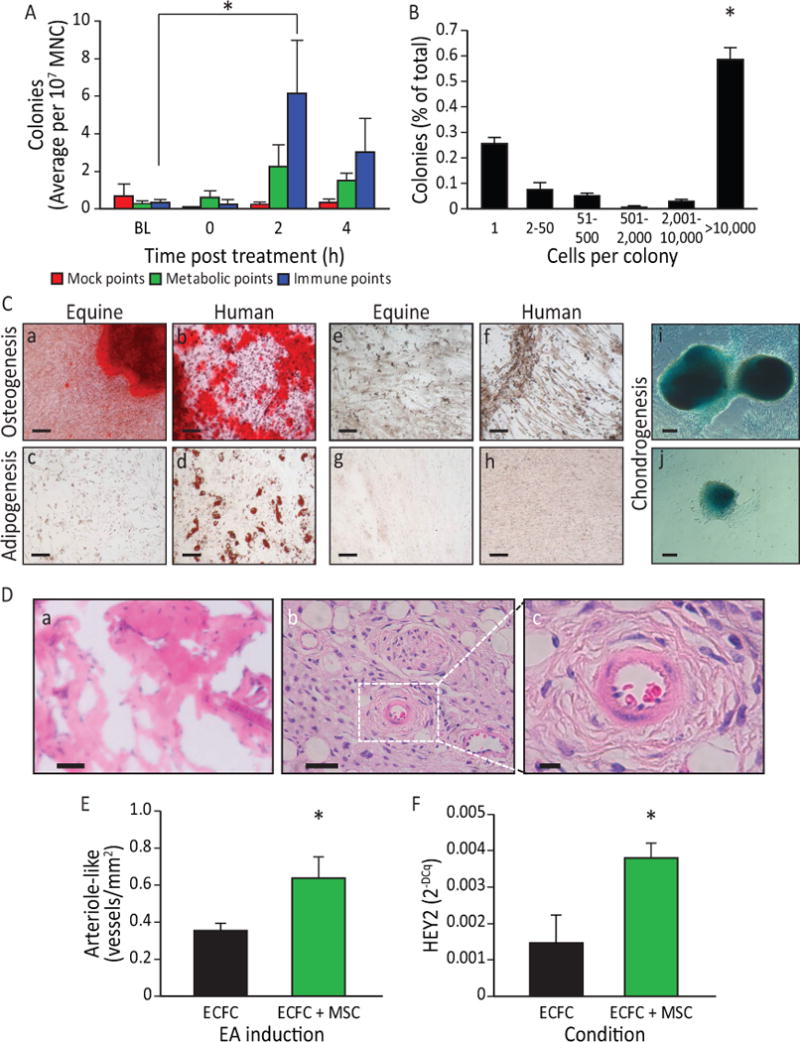
A) EA mobilized cells are highly proliferative and potentiate vasculogenesis. Equine peripheral blood MNC showed an increased colony-forming ability 2 h (p<0.05) post administration of EA at immune points (n=7), while cells obtained from the same horses when they underwent mock treatment or treatment at metabolic points did not. B) The EA-mobilized cells demonstrated high proliferative capacity, when plated in a single-cell assay, with over 50% proliferating into large colonies (p<0.001 vs. all groups). C) Equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells were cultured to the third passage and then differentiated into key mesenchymal lineages. a) Following culture with osteogenic induction media, the mobilized equine cells showed strong osteogenic potency, demonstrated by Alizarin Red staining of calcium deposits (Red: Alizarin Red). b) Human mesenchymal cells responded in a similar fashion when cultured under identical conditions. Equine cells when cultured under control media (1:1 Ham’s F12 and Low Glucose DMEM, 15%FBS)(e) and human cells under control conditions (f) did not show Alizarin Red staining. c) The EA-mobilized equine cells showed a weak adipogenic response, demonstrated by Oil Red O staining of lipid deposits (Red: Oil Red O) when cultured under adipogenic conditions; d) human MSC showed a much stronger response than the equine cells when cultured under identical adipogenic conditions. Under control conditions, neither equine MSC (g) or human MSC (h) showed Oil Red O staining. i, j) When cells were cultured under chondrogenesis differentiation medium they were able to differentiate into chondrogenic lineages, demonstrated by Alcian Blue staining of proteoglycans in the cell masses. Magnification bars: 50 μm. D) In vivo angiogenesis assay. a) When equine cells were incorporated into a 3D type I pig skin collagen plug and placed under the skin of NOD/SCID mice no capillaries were formed. b) Human ECFC were inserted into the porcine collagen plugs together with equine MSC, and implanted into the flank of NOD/SCID mice. c) A higher magnification of the boxed area in b), showing a bona fide blood vessel. Magnification bars: a, b: 50 μm; c: 10 μm. E) When quantified, the hECFC-MSC had a significant increase of arteriogenesis compared to hECFC alone (p=0.02, n=5 for ECFCs alone, n=7 for combined hECFC-MSC group). F) After 48 h in vitro, cells were isolated, total mRNA was extracted and Hey2 expression levels were quantified by qRT-PCR. Hey2 was elevated in the mixed cell treatment when compared to ECFC alone (p=0.006, n=4). All data presented as means ± SEM.
