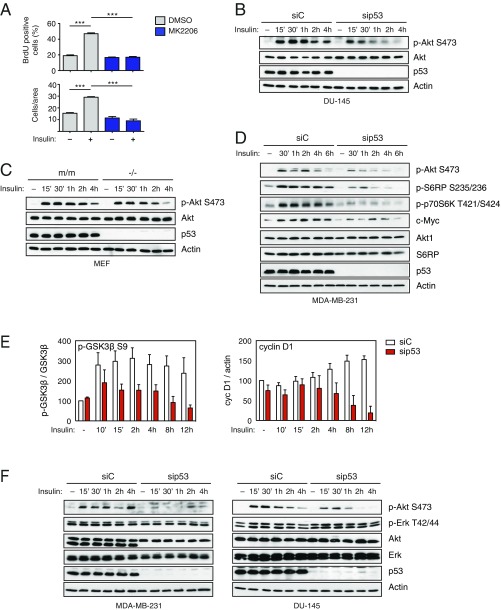
Fig. S3.
Mutant p53 specifically enhances insulin-induced AKT activation (related to Fig. 2). (A) Insulin-induced cell proliferation and invasion require AKT activity. DU145 cells were serum-starved and treated with insulin (0.5 μg/mL) for 24 h, with or without the specific AKT inhibitor MK2206 (5 μM). Proliferation and invasion assays were performed as in Fig. 1 (mean ± SEM; n = 3; ***P < 0.001). (B) Depletion of mutp53 reduces insulin-induced AKT activation in DU145 cells. Cells were transfected with control or p53 siRNA for 48 h, serum-starved for 24 h, and treated with insulin (0.5 μg/mL) for the indicated times. Phosphorylated AKT1 and total AKT1 were detected by immunoblotting. With actin as a loading control, p53 was blotted to verify knockdown efficiency. (C) Insulin-induced AKT activation is enhanced in mutant p53 knock-in MEFs. Ras-transformed MEFs derived from p53-null (−/−) or p53R172H knock-in (m/m) mice were used to analyze insulin-induced Akt (p-S473) activation. Phosphorylated AKT1 and total AKT1 were detected by immunoblotting. With actin as a loading control, p53 was blotted to verify knockdown efficiency. (D) Depletion of mutp53 affects insulin-induced AKT-dependent molecular responses. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated as in B. Phosphorylated AKT1 and total AKT1, S6RP, p70S6K, and c-Myc were detected by immunoblotting. With actin as a loading marker, p53 was blotted to control knockdown efficiency. (E) Depletion of mutp53 reduces insulin-induced phosphorylation of GSK3β and accumulation of cyclin D1. Graphs summarize relative p-GSK3β S9/GSK3β and CycD1/actin ratios in MDA-MB231 cells treated with insulin for the indicated times (representative blots are shown in Fig. 2D), as measured by densitometry on autoradiography film (average ± SEM, n = 3). (F) Depletion of mutp53 has no detectable effects on MAPK activation in insulin-treated cancer cells. MBA-MD231 and DU145 cells were treated as in B. Phosphorylated AKT1 and total AKT1 and ERK were detected by immunoblotting. With actin as a loading control, p53 was blotted to verify knockdown efficiency.