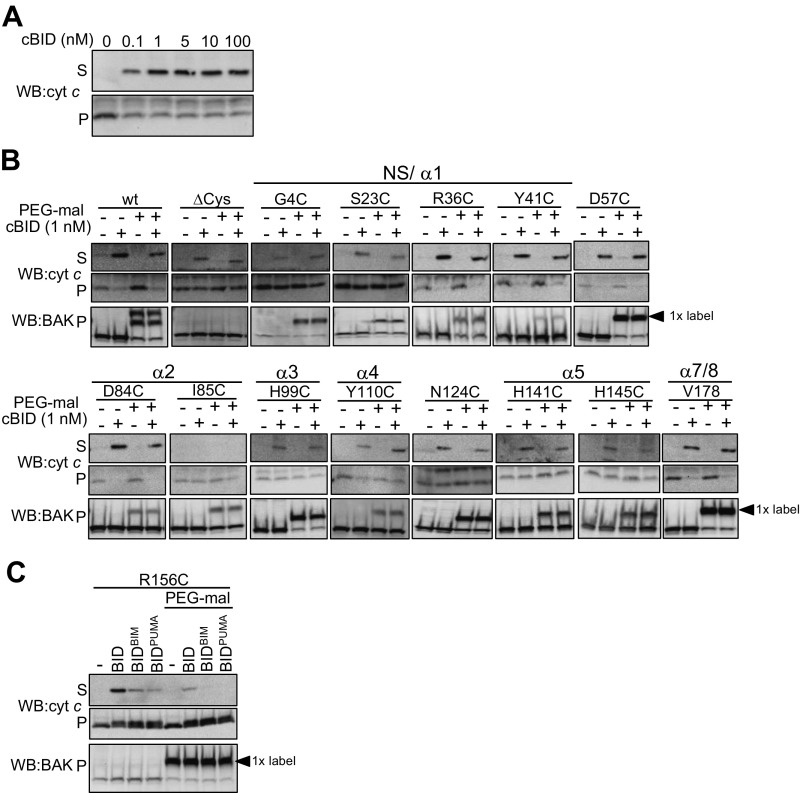
Fig. S6.
PEG-maleimide labeling commonly does not inhibit BAK activation induced by limiting concentrations of cBID. (A) Dose–response of cBID-induction of cytochrome c release. Mitochondrial fractions from Bak−/−Bax−/− MEFs expressing BAK were treated with the indicated concentration of cBID (30 °C, 30 min). Supernatant (S) and membrane (P) fractions were immunoblotted for cytochrome c. (B) Labeling does not inhibit BAK function in response to limiting dose of cBID. Mitochondrial fractions from Bak−/−Bax−/− MEFs expressing the indicated BAK mutants were treated with PEG-maleimide before treatment with cBID (1 nM, 30 °C, 30 min) for 30 min. Supernatant (S) and membrane (P) fractions were immunoblotted for cytochrome c and membrane fractions immunoblotted for BAK. (C) BAK activation induced by BIM and PUMA is inhibited by labeling the α6. Mitochondrial fractions from Bak−/−Bax−/− MEFs expressing BAK R156C were pretreated with PEG-maleimide before incubation with recombinant cBID or chimeras of cBID bearing the BH3 domain from BIM or PUMA and cytochrome c release was assessed as in A.