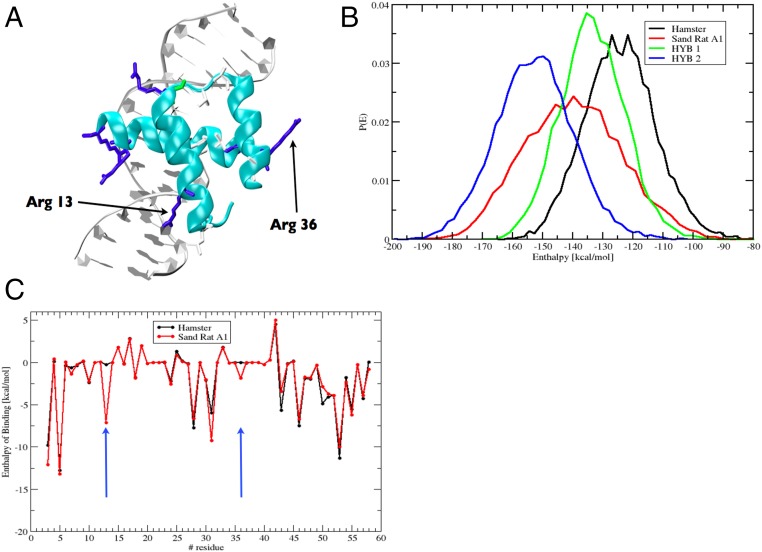
Fig. 3.
Molecular modeling of sand rat Pdx1 binding. (A) Molecular model of sand rat Pdx1 homeodomain bound to DNA. The two amino acid changes indicated are the largest contributors to altered enthalpy of binding. (B) Probability distributions of the enthalpy of binding of homeodomain protein–DNA interactions among hamster (normal vertebrate) Pdx1/mouse insulin A1 DNA element (black), sand rat Pdx1/sand rat A1 element (red), hamster Pdx1/sand rat A1 (green), and sand rat Pdx1/mouse A1 (blue) inferred by molecular dynamics simulations and MM-PBSA; sand rat Pdx1 homeodomain has the lowest enthalpy of binding (higher affinity) for each DNA target. (C) Per-site enthalpy of binding comparison between hamster and sand rat Pdx1 revealing contribution of amino acid changes at homeodomain positions 13 and 36 to reduced enthalpy of binding (higher affinity).