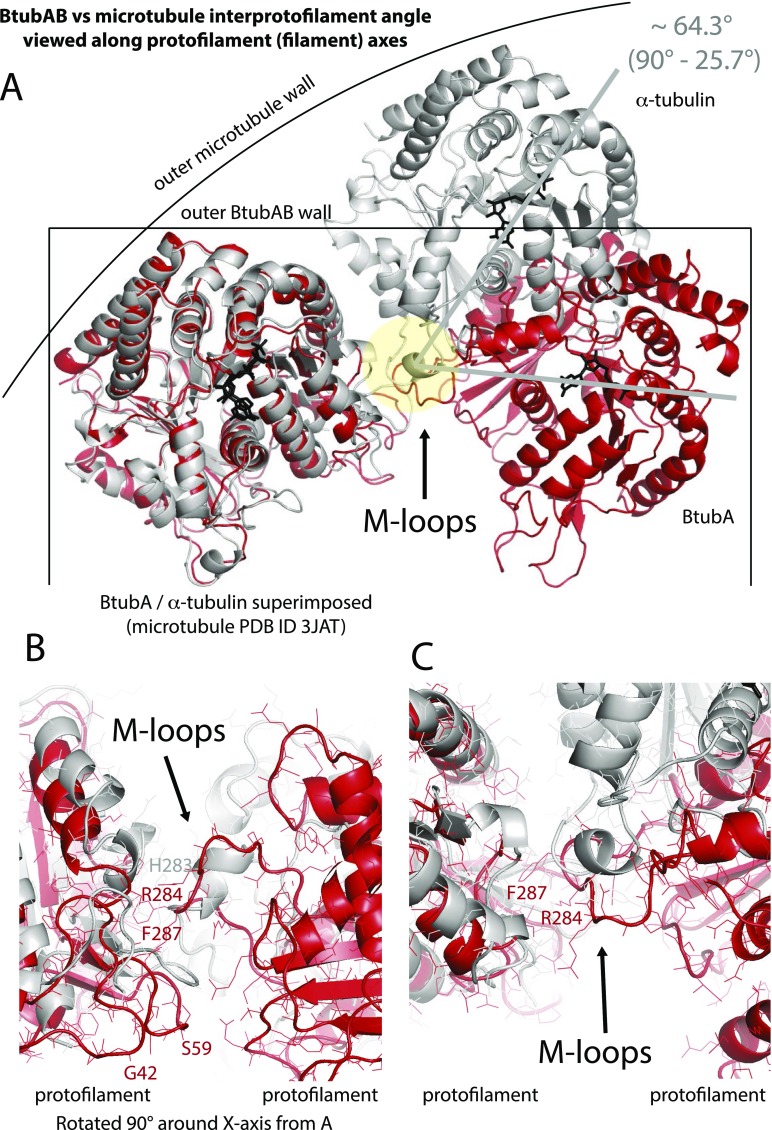
Fig. S5.
Comparison of interprotofilament interfaces in microtubules and BtubAB minimicrotubules. (A) Superposition of BtubA (red) and α-tubulin (gray) when in 4-protofilament BtubAB mini microtubules and 14-protofilament microtubules (PDB ID code 3JAT) (4). The protofilaments are rotated by ∼26° almost perfectly around the M loop, the structure in both polymers that facilitates protofilament contacts. (B and C) Detailed view of the same BtubAB/α-tubulin superposition showing the M loops. Although in roughly the same place, secondary structures are different and there is no obvious similarity of the contacts at the residues level. Divergent evolution probably changed the entire contact so to enable different interprotofilament angles, leading to 4 instead of more than 10 protofilaments. C is rotated 90° around the x axis with respect to B.