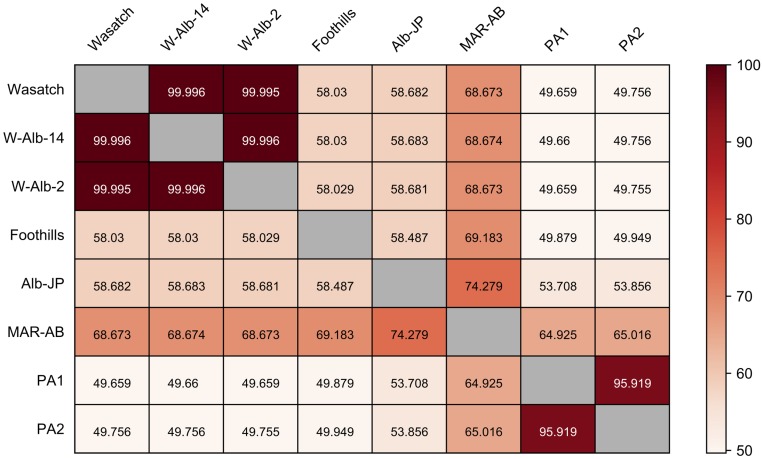
Fig. S3.
Similarity between strains as assessed with genome-wide SNP data. Values in each rectangle represent the percent similarity of pairs of strains as assessed with 488.6 thousand high quality SNPs (SI Materials and Methods) (percentage similarity for each comparison is color-coded according to the gradient at the far right). Strain names are at the left and across the top. Strains Wasatch, W-Alb-2, and W-Alb-14 are essentially identical, reflecting the inbred nature of Wasatch, and the origin of the two albino mutations on the Wasatch background (W-Alb-2 and W-Alb-14). The high level of similarity between PA1 and PA2 suggests that their progenitor Alb-NL strain was partly, but not completely, inbred at the start of the experiment (the strain had been maintained in the laboratory for more than 40 y and presumably lost genetic variation as a result of bottleneck events). Other strains show much reduced levels of identity to other strains, with Alb-NL and Alb-JP being comparatively dissimilar (reflecting an independent origin of albinism in these two strains). Although most strains are inbred or partly inbred, MAR-AB is highly outbred, potentially reflecting its apparent greater level of similarity to most other strains in the pairwise comparisons (SI Materials and Methods).