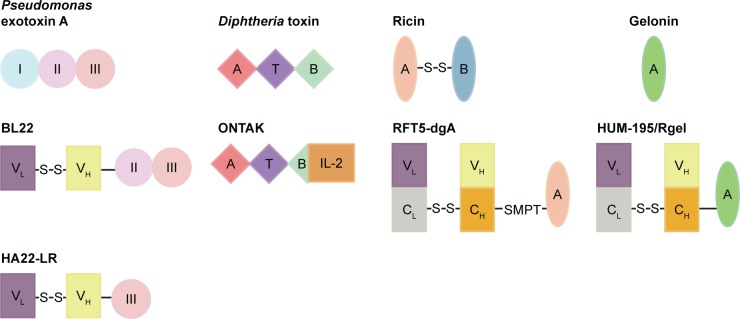
Figure 1.
Structure of widely used toxins and immunotoxins based on them.
Notes: Native PE A contains 3 functional domains: domain Ia (binding domain), domain II (mediates translocation of the toxin), and III (catalytic domain). BL22, which is also called CAT3888 or RFB4(dsFv)-PE38, is produced by replacing the domain I with a single-chain Fv target CD22. VL and VH are linked by disulfide bond. In its second generation of mutant, HA22-LR, most of domain II was deleted and PE amino acids 251–394 were replaced by 274–284. DT also contains 3 domains: A (enzymatic domain), B (binding domain), and T (transmembrane domain). In ONTAK, a recombinant human IL-2 was fused to the C-terminus of the toxin. Ricin is a plant toxin that belongs to holotoxins and has both enzymatic domain (A) and binding domain (B). RFT5-dgA is formed by a monoclonal antibody target CD25 and a deglycosylated ricin A chain. A hindered heterobifunctional cross-linker links the antibody and toxin. Gelonin only has enzymatic domain (A). HUM-195/Rgel contains a recombinant gelonin conjugated to a humanized antibody target CD33.
Abbreviations: PE, Pseudomonas exotoxin; DT, Diphtheria toxin; IL-2, interleukin-2; Rgel, recombinant gelonin; dgA, deglycosylated ricin A chain; SMPT, N-succimidyl-oxycarbonyl-α-methyl-α-(2-pyridyldithio)-toluene.