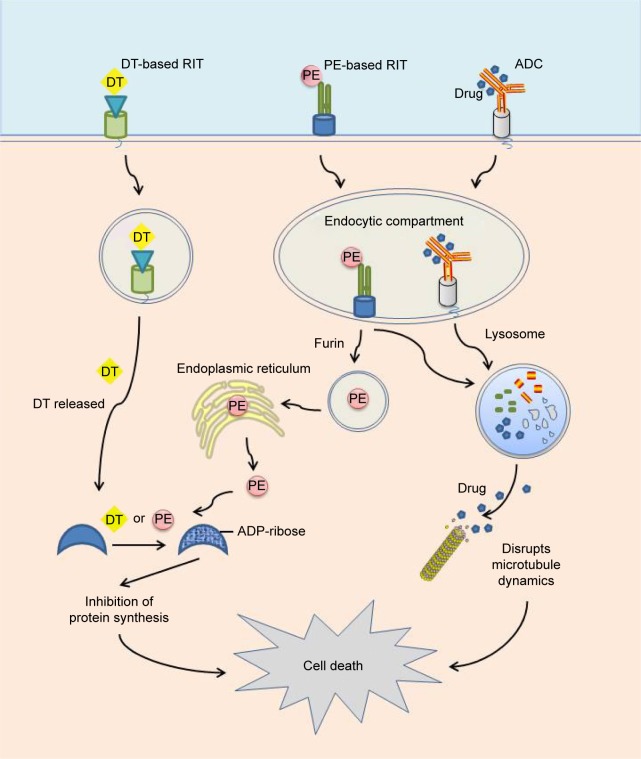
Figure 2.
Mechanism of ADCs and immunotoxins based on PE A and DT.
Notes: ADCs and immunotoxins are internalized into an endocytic compartment after binding on the cell surface. The ADCs travel to lysosomes, where the drug is released from the antibody, inducing drug penetration in the cytosol, disruption of microtubule dynamics, and cell death. Modified PE toxin is cleaved from immunotoxin by the furin protease and transported to the ER through the Golgi. The toxin catalyzes ADP ribosylation of eEF2, inducing inhibition of protein synthesis and cell death. The T domain of DT forms a pore in the membrane of the endosome, allowing transit of DT in the cytosome. DT also catalyzes inhibitory modification of eEF2.
Abbreviations: ADC, antibody–drug conjugate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PE, Pseudomonas exotoxin A; DT, Diphtheria toxin; ADP-ribose, adenosine diphosphate ribose; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; RIT, recombinant immunotoxins.