Figure 3.
Development of the PE-based immunotoxins to increase the toxicity and to decrease the immunogenicity.
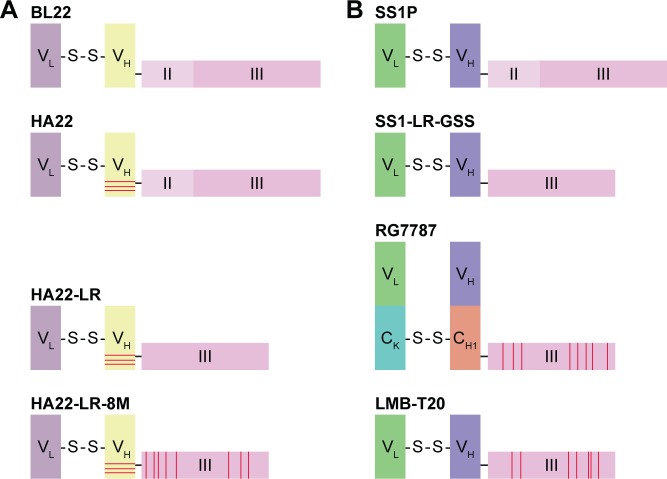
Notes: (A) RITs targeting CD22. (B) RITs targeting MSLN. BL22, also named RFB4(dsFv)-PE38 and CAT-3888, contained a single-chain Fv of the anti-CD22 antibody fused to truncated PE toxin. HA22 was mutated from BL22 by replacing the residues at positions 100, 100a, and 100b of VH, represented here by horizontal red bars. In HA22-LR, the deletion mutant, most of domain II of PE toxin was deleted. HA22-LR-8M, a mutant of HA22-LR, was reported to contain 8 mutations, D406A, R432G, R467A, R490A, R513A, E548A, K590S, and Q592A. SS1P consists of the Fv fragment from anti-MSLN monoclonal antibody coupled to the same PE fragment with BL22. SS1-LR-GGS was developed by deleting the domain II of PE toxin with GGS linker between the antibody and the domain III. RG7787 used a humanized Fab fragment of anti-MSLN antibody and deleted PE domain II. In RG7787, there were 7-point mutations in domain III of PE toxin at B-cell epitopes to eliminate binding to B-cell receptor. LMB-T20 consisted of the Fv fragment coupled to the similar PE fragment with RG7787, but with 6-point mutations in domain III at T-cell epitopes.
Abbreviations: PE, Pseudomonas exotoxin A; RIT, recombinant immunotoxins; MSLN, mesothelin.