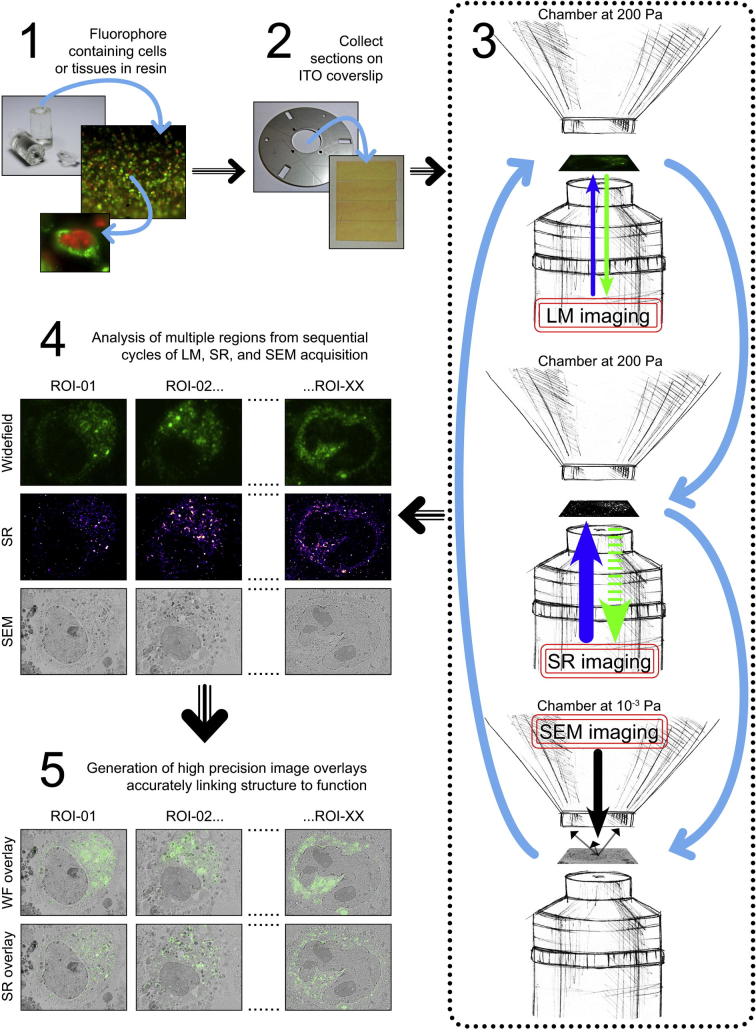
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustrating the typical workflow for WF, SR and EM imaging (modified from Brama et al. (2015)). Specimens were first processed for high pressure freezing and quick freeze substitution as described in Peddie et al. (2014), embedded in acrylic resin, and collected as 200 nm serial sections on an ITO-coated glass coverslip. The coverslip was attached to a SECOM specimen holder, and placed on the SECOM microscope stage. The SEM chamber was pumped to 200 Pa, and WF and SR image acquisition for a specific region of interest was carried out before pumping to high vacuum for SEM BSE image acquisition; after which, the vacuum pressure could be cycled to allow for multiple rounds of image acquisition from several regions of interest within the same specimen, or across serial sections using an array tomography workflow.