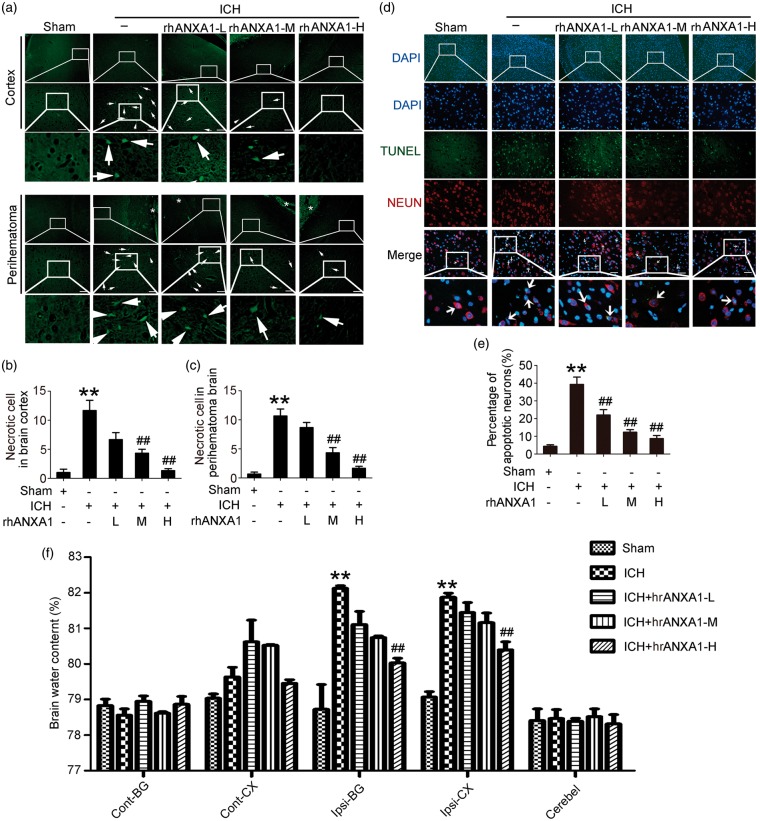
Figure 4.
Effects of exogenous ANXA1 on neuronal degradation and death, and brain water content under ICH conditions. (a) Fluoro-Jade B (FJB) staining (green) shows neuronal degradation in cerebral cortex and perihematoma brain. Scale bar = 100 µm. Arrows point to FJB-positive cells. FJB-positive cells/mm2 was quantified in brain cortex (b) and perihematoma brain (c), respectively. (d) Double immunofluorescence for NeuN (red) and TUNEL (green) counterstained with DAPI (blue) was performed. Arrows point to apoptotic neurons, namely NeuN/TUNEL-positive cells. Scale bar = 100 µm. Percentage of TUNEL-positive neurons was shown (e). (f) Bar graphs showing the effects of rhANXA1 on brain water content. Cont: contralateral; Ipsi: ipsilateral; CX: cortex; BG: basal ganglia; Cerebel; cerebellum. In (b,c,e,f), one-way ANOVA followed by Student–Newman–Keulspost hoc tests were used. Data are means ± SEM. **p < 0.01 vs. sham group, ##p < 0.01 vs. ICH group, n = 6. rhANXA1-L: 0.34 µg/kg body weight; rhANXA1-M: 0.67 µg/kg body weight; rhANXA1-H: 1.34 µg/kg body weight.