Figure 1. The BBB and the glia limitans together limit the migration of inflammatory leukocytes from the blood into the CNS.
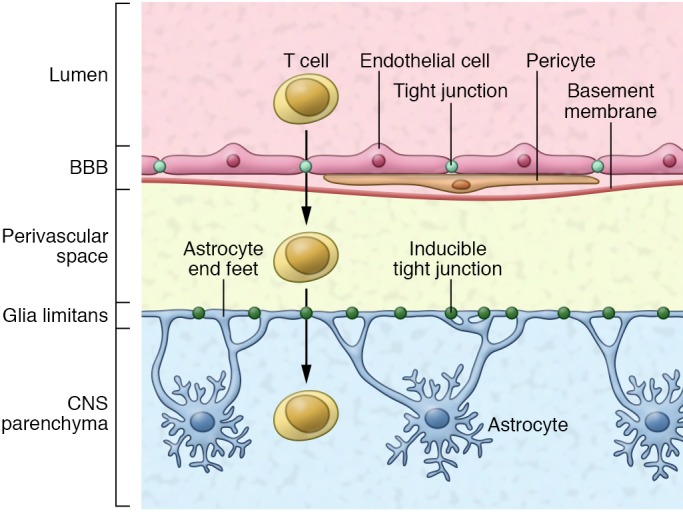
The BBB is formed by endothelial cells connected by tight junctions and surrounded by a basement membrane with pericytes interspersed. The glia limitans serves as a second barrier that is formed by astrocytic endfeet processes. In this issue, Horng et al. reveal that tight junction formation in the glia limitans is induced in response to inflammation and serves as a secondary barrier to limit infiltration of activated T cells into the CNS.
