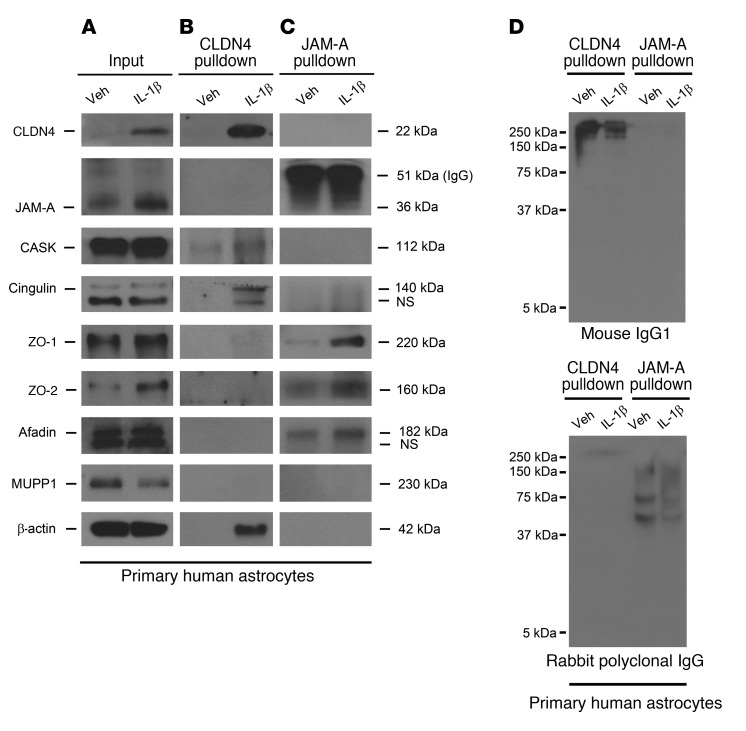
Figure 3. CLDN4 and JAM-A coimmunoprecipitate with canonical TJ complex proteins.
(A–C) Immunoprecipitation of cell lysates from cultured human astrocytes under control and IL-1β–treated conditions reveals that CLDN4 and JAM-A bind different patterns of intracellular TJ adaptor proteins. (A) Cell lysate inputs confirm that astrocytes upregulate JAM-A and CLDN4 after IL-1β treatment and express a variety of intracellular TJ adaptor proteins at baseline and under IL-1β–treated conditions. (B) CLDN4 associates with cingulin, CASK, ZO-1 (the latter weakly), and β-actin. (C) JAM-A complexes with an overlapping but slightly different array of TJ-associated proteins, including ZO-1, ZO-2, afadin, and cingulin (the latter weakly). Interestingly, and compatible with previous reports (30), CLDN4 and JAM-A do not coimmunoprecipitate with each other, suggesting that the 2 proteins do not associate directly and, if connected at all, are linked via weaker bonds of intermediary proteins. (D) Nonspecific isotype control mouse IgG1 and polyclonal rabbit IgG do not show signal at the molecular weights corresponding to TJ-associated proteins of interest, confirming that antibodies for TJ adaptor proteins are specific. Data are representative of findings from more than 3 biological replicates (A–D).