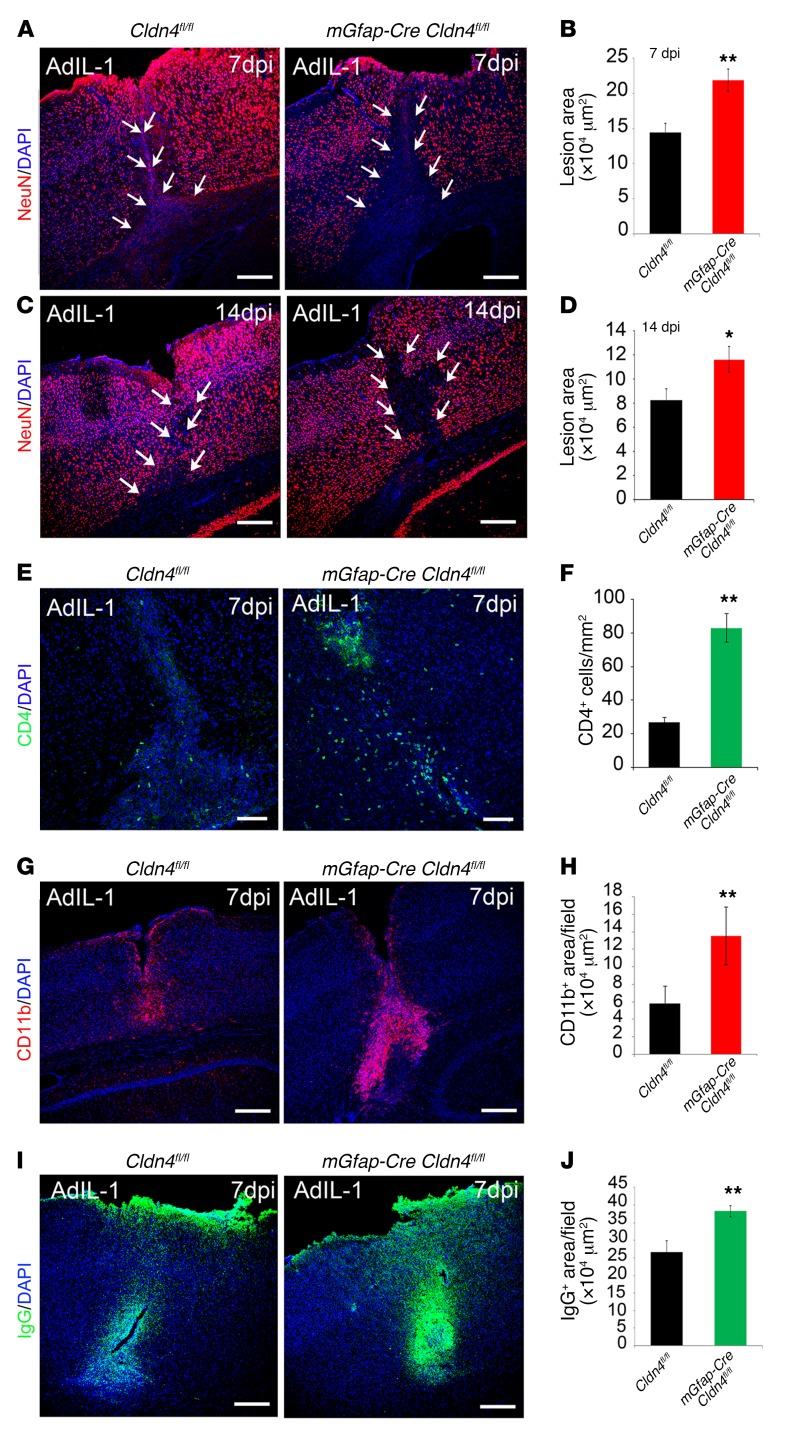
Figure 5. Conditional astrocyte Cldn4 inactivation exacerbates the size of inflammatory CNS lesions.
Cortical AdIL-1 microinjection produces asymptomatic inflammatory lesions characterized by leukocyte (predominantly CD4+ and CD11b+ cell) and humoral factor parenchymal entry, accompanied by reactive astrogliosis and neuronal death. Lesion pathogenesis peaks at 7 dpi and is resolving by 14 dpi. (A–D) Compared with controls, Cldn4 CKO mice display increased AdIL-1 lesion size, as measured by the area of neuronal cell death (NeuN loss), at 7 dpi and 14 dpi (7 dpi: n = 12 CKO, n = 15 WT, P < 0.005; 14 dpi: n = 5 CKO, n = 8 WT, P < 0.05, 2-tailed t test). Scale bars: 300 μm. (E–H) At 7 dpi, lesions of Cldn4 CKO mice have increased numbers of CD4+ lymphocytes (n = 10 CKO, n = 10 WT, P < 0.01, 2-tailed t test) (E and F) and level of CD11b+ staining (n = 6 CKO, n = 9 WT, P < 0.005, 2-tailed t test) (G and H). (I and J) At 7 dpi, lesions of Cldn4 CKO mice show increased areas of IgG entry (n = 8 KO, n = 11 WT, P < 0.01, 2-tailed t test). See also Supplemental Figure 3, A–G. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.