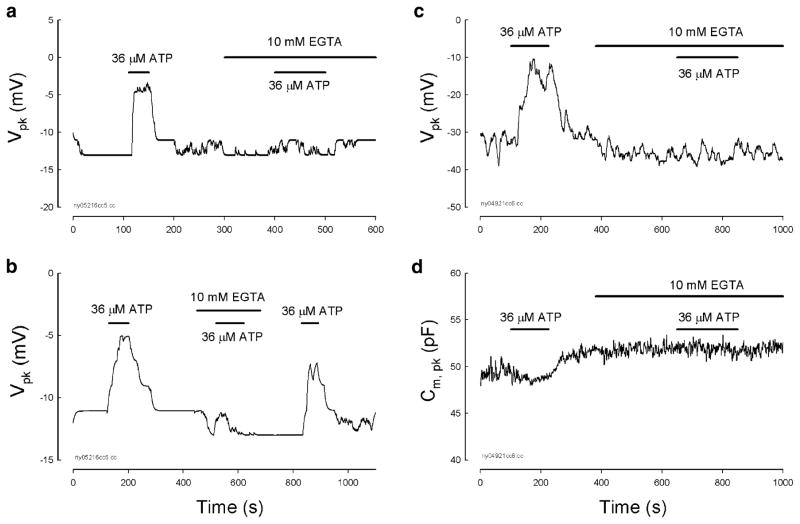
Fig. 5.
Extracellular Ca++ is required for ATP-modifying OHC electromotility-associated NLC. a and b The patch pipette was filled with normal intracellular solution and the bath was perfused with NES. Removal of extracellular Ca++ ions by application of 10 mM EGTA Ca++-free extracellular solution eliminated the ATP effect. The elimination is reversible. Reperfusion of NES restored the ATP effect (b). c and d Ineffectiveness of intracellular Ca++ on the ATP effect. The patch pipette was filled by the intracellular solution with 10 mM BAPTA to chelate intracellular Ca++ concentration; intracellular K+ was also replaced with Cs+ (140 CsCl, 10 BAPTA, 2 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES in mM). The bath was perfused with NES. The effect of ATP on NLC remained. Extracellular perfusion of 10 mM EGTA also abolished the ATP effect