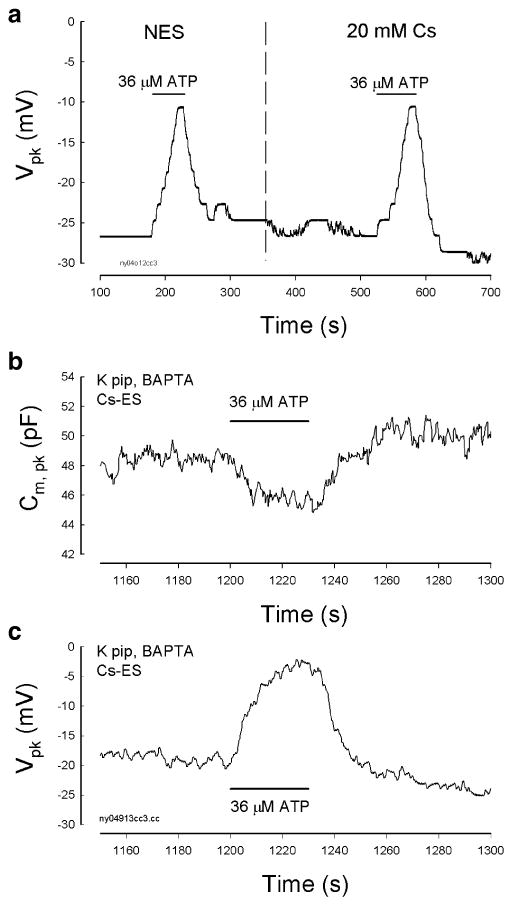
Fig. 6.
Independence of the ATP effect on K+ and Na+. a The effect of ATP is independent of K+ ions. The dashed vertical line indicates that an OHC was alternatively perfused with NES and 20 mM Cs+ extracellular solution (130 NaCl, 20 CsCl, 2 CaCl2, 1.47 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES in mM) to replace extracellular K+. The patch pipette was also filled with 140 mM Cs+ to replace K+ (Cs pipette: 140 CsCl, 10 EGTA, 2 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES in mM). b and c The effect of ATP on OHC electromotility-associated NLC is independent of extracellular Na+. The patch pipette was filled with a BAPTA-buffered intracellular solution. The OHC was perfused with a Cs-based extracellular solution (Cs-ES), which Na+ and K+ were replaced with 140 mM Cs+ (140 CsCl, 2 CaCl2, 1.47 MgCl2, and 10 HEPES in mM)