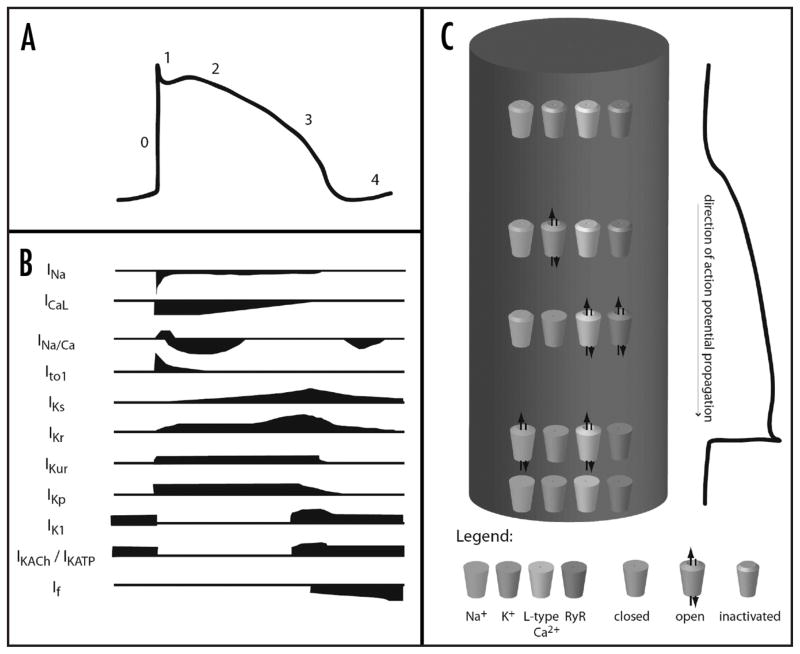
Figure 2.
The contributions of various ionic currents to an action potential. (A) demonstrates the changes in transmembrane potential that occur during an action potential. (B) indicates the currents of sodium (INa), calcium (ICaL), and potassium (IK…) that occur during the course of the action potential. (C) diagrams in a very general way the channel openings, closings, and inactivations that occur during an action potential, where the cylinder represents a single myocyte. (A and B) adapted with permission from Tamargo19.