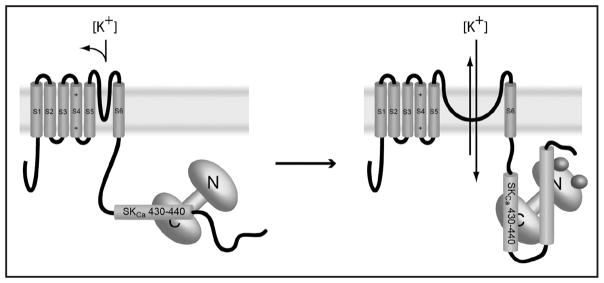
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanism for calcium dependent activation of SKCa channels. Closed channels, at left, constitutively bind the C-lobe of calmodulin. Calcium binding causes a >90° rotation in the 430–440 segment of the SKCa C-terminus, altering the conformation of S6 and gating the channel to the open position. Calcium binding also causes a significant ordering of other parts of the C-terminus as well; the crystal structure of Ca-CaM with the SKCa-CTD is a domain swapped dimer with both lobes of CaM binding different parts of the SKCa-CTD.