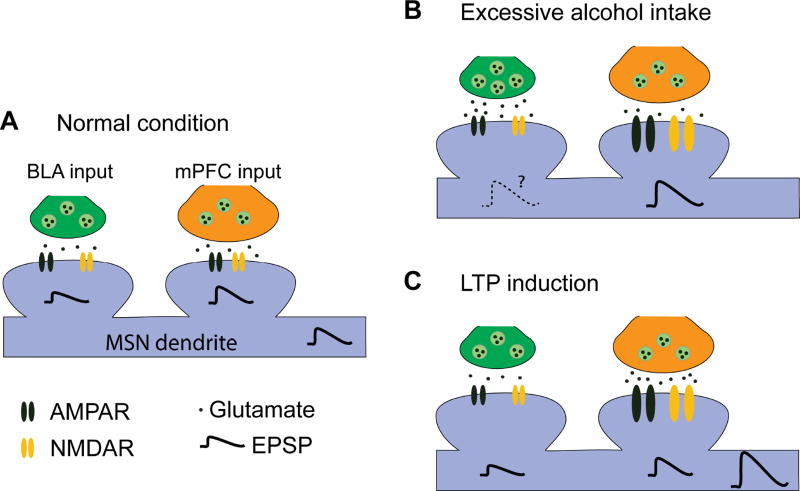
Fig. 7. Schematic illustrating the mPFC and BLA inputs to DMS MSNs and their responses to excessive alcohol intake and LTP induction.
(A) In the normal condition, MSNs receive mPFC and BLA inputs with a great extent from the mPFC. (B) Excessive alcohol consumption potentiates AMPAR and NMDAR activities (as shown by the larger receptor size) at the mPFC input, as well as the probability of glutamate release at the BLA input. These changes cause enhancement of CortSt and possibly AmygSt transmission. (C) Paired stimulation of the mPFC and BLA inputs leads to large membrane depolarization and reliable LTP induction at the mPFC input.