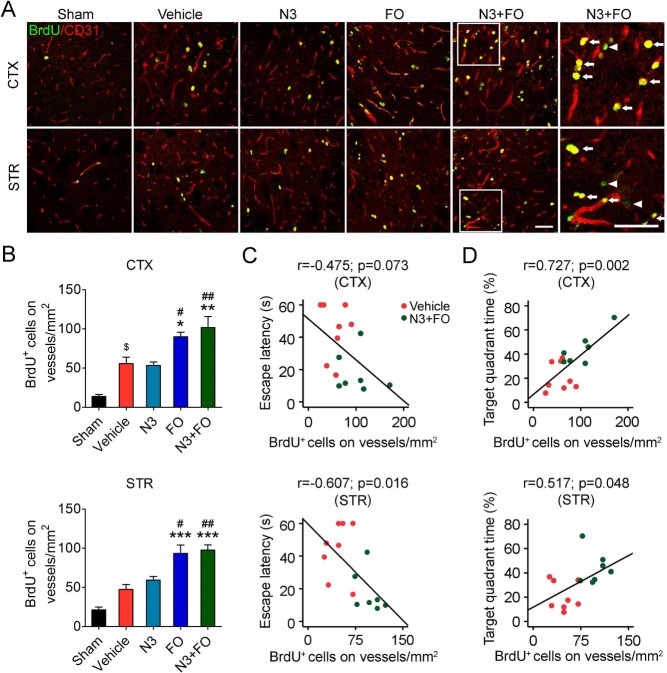
Figure 5.
Delayed n-3 PUFA treatment promotes post-TBI angiogenesis. (A) Representative images of 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) and CD31 immunofluorescence in the ipsilateral perilesion cortex (CTX) and striatum (STR) at 35 days after traumatic brain injury (TBI). Boxes indicate areas that were enlarged in high-power images (the sixth column). Arrows: BrdU+ cells on vessels (yellow) Arrowheads: BrdU+/CD31− cells (green). Scale bars: 50 μm. (B) Quantification of newly generated endothelial cells (BrdU+/CD31+ cells) in the perilesion cortex and striatum. $p ≤ 0.05 versus sham; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 versus vehicle; #p ≤ 0.05, ##p ≤ 0.01 versus N3 (fatty acid injection) by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). (C, D) Pearson correlation between the mice's spatial learning (C) and memory (D) performance in the Morris water maze and the numbers of BrdU+/CD31+ cells in cortex and striatum. n = 6 mice for sham group; n = 8 mice for vehicle, N3, and fish oil dietary supplementation (FO) groups; n = 7 mice for N3 + FO group.