Figure 1.
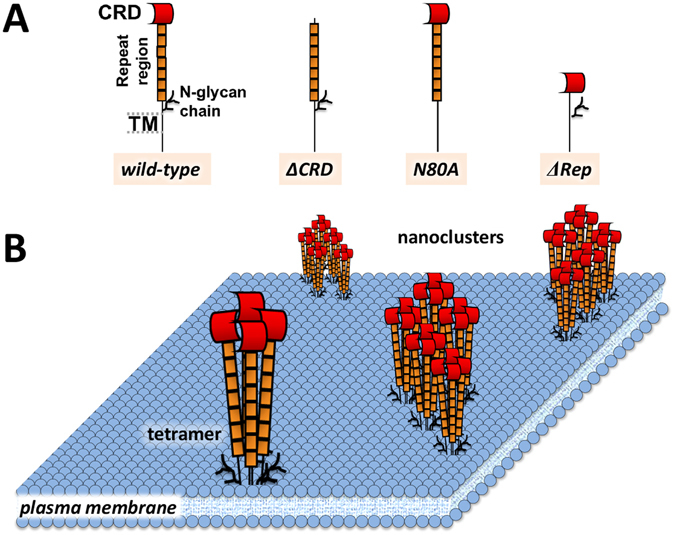
Structure and membrane nanoscale organization of DC-SIGN. (A) DC-SIGN is type-II C-type lectin (N-terminus is intracellular) that has an extracellular Carbohydrate Recognition Domain (CRD), a region of 7.5 amino acid repeats, preceded by a site for N-glycosylation (amino acid N80), a transmembrane region and a short cytoplasmic tail. In this study, besides the wild-type, several mutants of DC-SIGN were used: DC-SIGN-ΔCRD, which lacks the ligand binding domain; DC-SIGN-N80A, which carries a point mutation that abolish N-glycosylation; and DC-SIGN-ΔRep, which only lacks the repeat region25. (B) Except for DC-SIGN-ΔRep, all the other variants can form tetramers and organize in small nanoclusters within the plasma membrane10.
