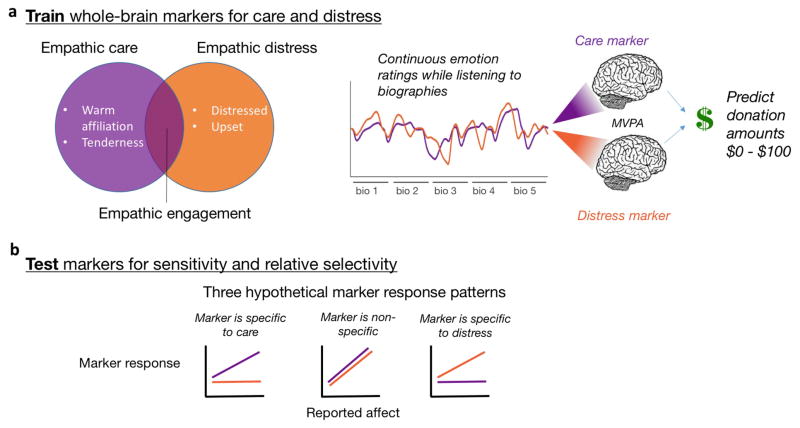
Figure 1.
Theoretical and analytic framework. (a) The encounter with a suffering person can elicit both empathic care and empathic distress. Participants provided continuous ratings of these emotions while listening to biographies describing true stories of human suffering. We developed whole-brain patterns predicting ratings of empathic care and distress from fMRI activity, and used marker responses to predict real-money trial by trial charitable donation amounts. (b) In leave-one-out cross-validation, we tested the sensitivity and relative selectivity of both markers, applying them to held-out test data for empathic care and distress.