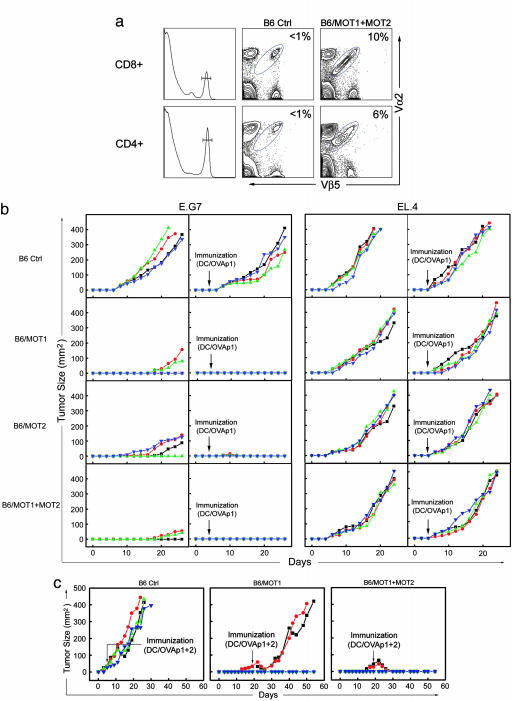
Fig. 4.
In vivo constitution of anti-tumor T cell immunity. E.G7 mouse tumor model was used. Tumor size is shown as the product of the two largest perpendicular diameters a × b (mm2). Each line represents one mouse. Four mice were included in each group, and experiments were performed three times. Results from one representative experiment are shown. (a) Constitution in mouse of both arms of anti-tumor T cell immunity. FACS staining showed the detection of mature OT1 CD8 and OT2 CD4 T cells in the spleen of B6/MOT1+MOT2 mice (B6 mice receiving both MOT1- and MOT2-transduced WT HSCs). (b) Suppression of syngenic tumor growth by in vivo constitution of anti-tumor T cell immunity. EL.4 and its OVA-expressing derivative, E.G7, were the two mouse tumor types examined. DC/OVAp1, DCs loaded with OVAp1. (c) Eradication of established solid tumors by in vivo constitution of both arms of anti-tumor T cell immunity. E.G7 tumor cells were used. DC/OVAp1+2, DCs loaded with both OVAp1 and OVAp2.