Figure 7.
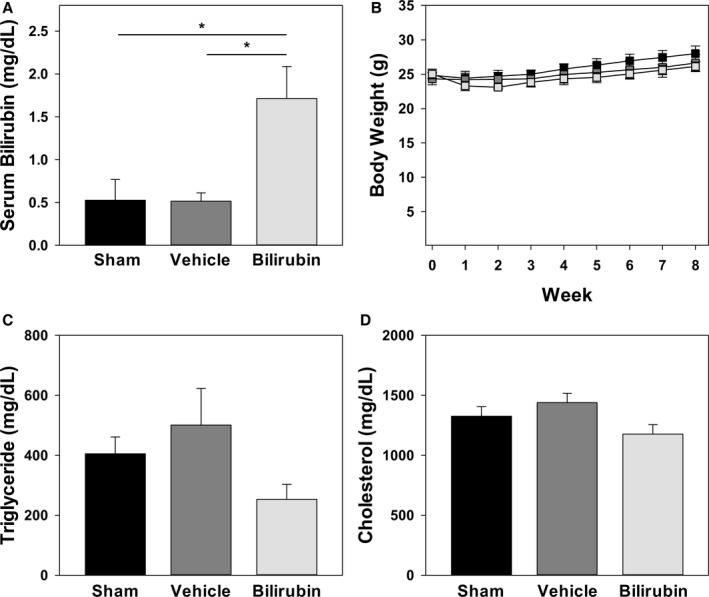
Effect of bilirubin administration on body weight, serum bilirubin, and lipid levels. A, Serum bilirubin levels in chow‐fed C57BL/6J mice that were administered intraperitoneal injections of bilirubin (30 mg/kg), vehicle, or sham once‐daily for 5 days. Bars reflect the mean (±SEM) for each treatment group (n=5–6). B, Body weights of Western diet–fed Ldlr −/− mice receiving intraperitoneal bilirubin (light gray symbols), vehicle (dark gray symbols), or sham (black symbols). Data points reflect the mean (±SEM) for each treatment group (n=4–7). C and D, Serum triglyceride and cholesterol levels, respectively, in Ldlr −/− mice after 8 weeks on a Western diet, with bars reflecting the mean (±SEM) for each treatment group (n=4–7). Although not statistically significant, bilirubin‐treated mice exhibited a strong trend toward reduced serum triglyceride concentrations when compared to sham (P=0.066) and vehicle (P=0.053) groups. *P<0.05.
