Figure 1.
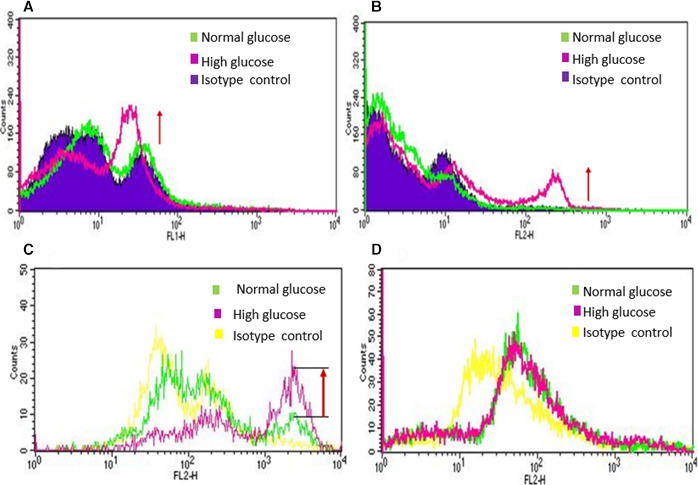
Fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis of EPCs (CD34+) and HUVECs exposed to normal glucose (NG) and high glucose (HG): Human EPCs (CD34+) were exposed to NG (5.5 mmol/L) and HG (20 mmol/L) for 48 hours followed by FACS Analysis. A, Annexin V stained cells and B, Propidium iodide stained EPCs (CD34+) demonstrated significant degree of apoptosis takes place within 48 hours of high glucose exposure. To compare effect of NG and HG on endothelial progenitor and mature endothelial cells, C, human EPCs (CD34+) and D, HUVECs were exposed to NG and HG for 48 hours and 10 days, respectively, and cells were stained with propidium iodide. EPCs (CD34+) showed increased apoptosis by 48 hours of high glucose exposure. However, HUVECs did not show any apoptotic change even after 10 days of HG exposure compared to NG exposed cells. These data demonstrate that EPCs are more susceptible to HG mediated injury compared to mature endothelial cells (HUVECs).
