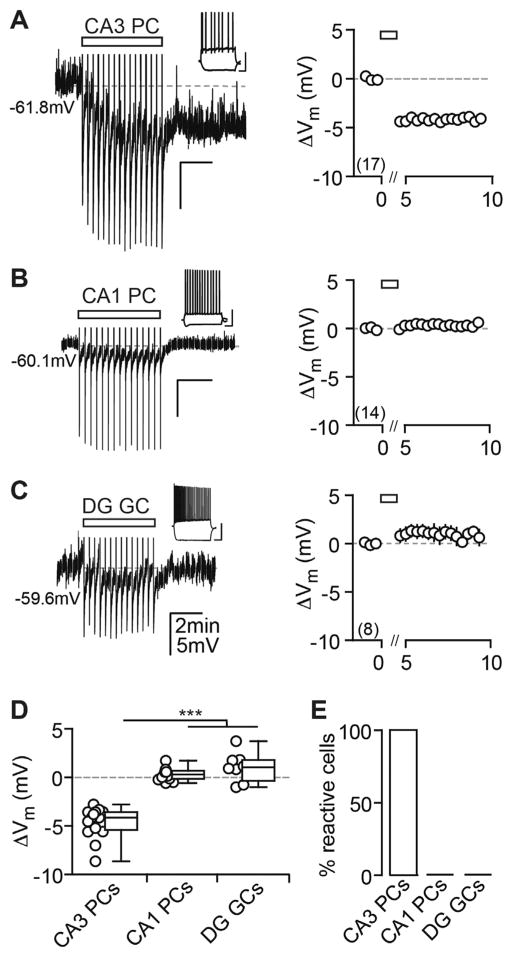
Figure 1. AP Firing Induces a Cell Type-Specific Vm Hyperpolarization in Hippocampal Principal Cells.
(A–C) Current injection-triggered AP trains (rectangle) induce a long-lasting Vm hyperpolarization in CA3 PCs (A), but not in CA1 PCs (B) and DG GCs (C). Left: exemplary pp recordings of each principal cell population are shown. APs have been truncated and test pulses cut for display purposes in this and all later figures. Insets: firing patterns are shown (scale bar, 40 mV, 0.2 s). Right: summary time course shows the ΔVm average for CA3 PCs: n(N) = 17(13), CA1 PCs: n(N) = 14(4), and DG GCs: n(N) = 8(4). The x axis is discontinued for the duration of the AP train.
(D) The ΔVm of each recorded cell (circles) and the median and 25th and 75th percentiles of the average ΔVm calculated from the first minute after the last AP train are shown for CA3 PCs (−4.1, −5.4, and −3.6 mV), CA1 PCs (0.30, −0.15 to 0.68 mV) and DG GCs (1.04, −0.35 to 1.8 mV). Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s post-test, p < 0.05 for CA3 PCs versus CA1 PCs and DG GCs.
(E) Percentage (%) of reactive cells is shown.