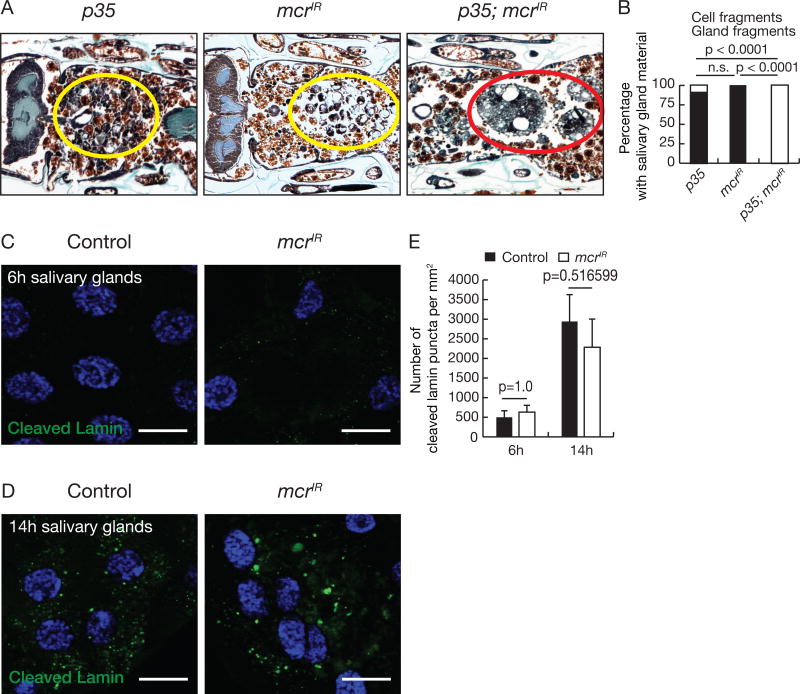
Figure 2. mcr functions in an additive manner with caspases during salivary gland degradation.
(A) Animals with salivary gland-specific p35 expression (n = 16), mcr knockdown (n = 24), and p35 expression plus mcr knockdown (n = 25) analyzed by histology for the presence of salivary gland material at 24h after puparium formation. Yellow circles, cell fragments; red circle, salivary gland fragments.
(B) Quantification of data from (A). Statistical significance: Chi-square test.
(C and D) Salivary glands dissected 6h (C) and 14h after puparium formation (D) from control animals and those with salivary gland-specific mcr knockdown, stained with anti-cleaved Lamin antibody (green) and Hoechst (blue). Scale bars, 50 µm.
(E) Quantification of data from (C and D). Error bars, mean ± SEM; n = 12 (control 6h), n = 10 (control 14h), n = 10 (mcrIR 6h), n = 14 (mcrIR 6h). Statistical significance: Student’s t-test.
See also Figure S2.