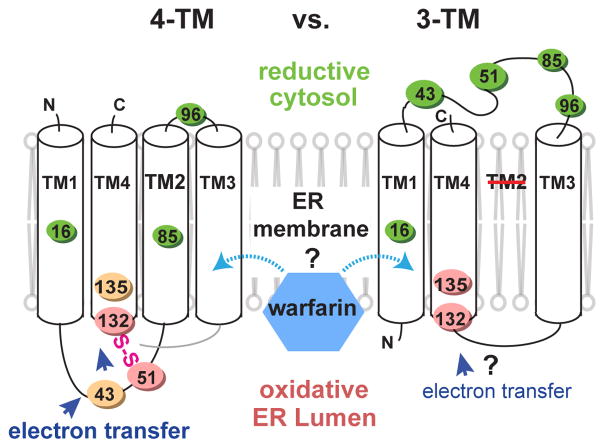
Figure 1. Alternative models of hVKOR architecture to explain warfarin interaction and electron transfer.
Left, four-TM model. Cys43, Cys51, Cys132, and Cys135 are oxidized (orange and pink colors stand for oxidation levels observed in Fig. 2b) at the ER luminal side. Interactions between these four conserved cysteines permits electron transfer (blue arrows). Right, three-TM model. Cys43 and Cys51 are reduced (green) at the cytosolic side and separated from Cys132 and Cys135, and therefore cannot mediate electron transfer.