Figure 1.
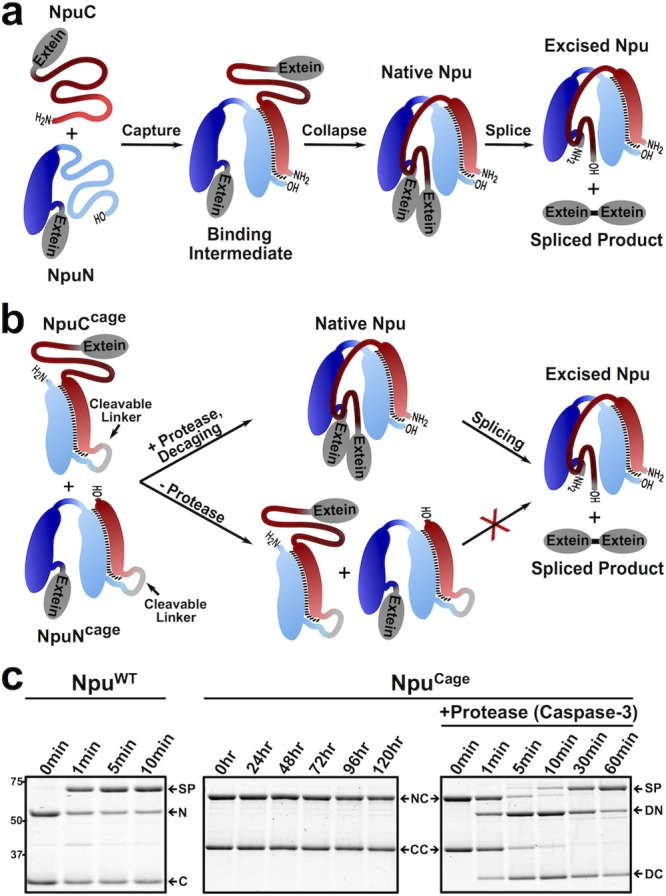
Design and characterization of caged intein zymogens: N = MBP-NpuN, C = NpuC-eGFP, NC = MBP-NpuNCage, CC = NpuCCage-eGFP, DN = decaged-NC, DC = decaged-CC, SP = splice product (MBP-eGFP). (a) Schematic depicting two-step mechanism by which the split fragments of Npu (NpuC and NpuN) assemble and splice. (b) Schematic depicting the design of NpuCCage and NpuNCage constructs, where addition of a protease cleaves or “decages” the inteins leading to protein splicing. (c) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels of splicing reactions (37 °C, 1 μM each intein fragment) monitored over time of either the wild-type (NpuWT) or zymogen (NpuCage) versions of the split Npu intein. Caspase-3 was added to a separate aliquot of NpuCage at time = 0 h.
