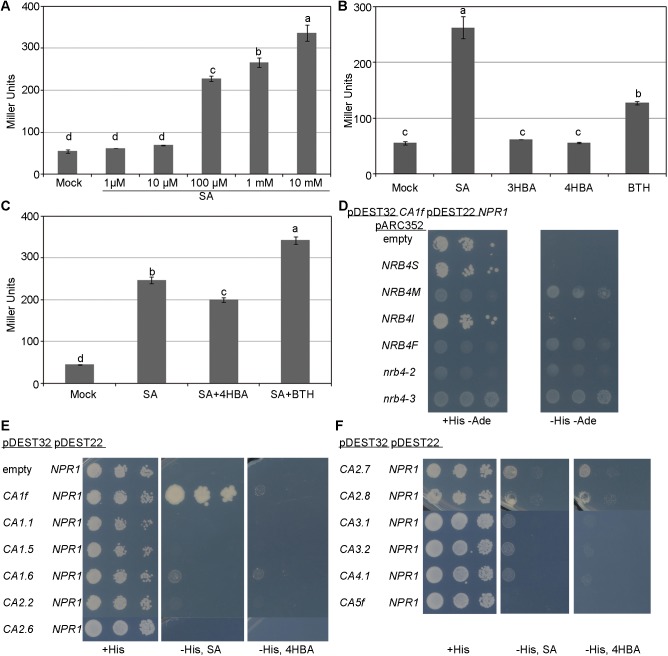
Fig 4. Quantification of the βCA1f-NPR1 interaction; other βCAs also interact with NPR1.
(A) Dose response to SA in the interaction between βCA1f and NPR1. Yeast containing both cDNAs was grown in the presence of SA, and β-galactosidase activity was then measured, since the interaction between the two cDNAs leads to the expression of this enzyme. (B) The βCA1f-NPR1 interaction requires a functional analog of SA; 3HBA represents 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, and the interaction was quantified as described in “A”. (C) The inactive analogs competed poorly with SA, while active analogs showed an additive effect. The interaction was quantified as described in “A”. In panels “B” and “C”, 100 μM of each chemical was added to the medium. (D) Yeast three hybrid. Several versions of NRB4, described in Fig 1, were cloned in a third plasmid and introduced into yeast with βCA1f and NPR1 to show a triple interaction. (E) Five additional βCAs were tested as in Fig 1C. (F) Six additional βCAs were tested as in Fig 1C. In total, βCA1.6, βCA2.2, βCA2.7, βCA2.8, βCA3.1, βCA3.2, and βCA4.1 also interacted with NPR1, although less strongly and not depending on SA, as is the case with βCA1f.