Abstract
Purpose
To explore the relationship between initial clinician type (generalist versus subspecialist) seen by infertile women, type of treatment received, and time to pregnancy.
Methods
In a retrospective cohort design, we analyzed mixed-mode questionnaire data from 867 women with primary infertility enrolled through population- and fertility clinic-based sampling. We compared women presenting first to generalist providers with women presenting first to fertility subspecialists, with the main outcomes of receiving in vitro fertilization (IVF), time to pregnancy, and live birth.
Results
The first point of contact for most (84%) women with infertility was a generalist provider. Only 8% of women sought care first from a fertility subspecialist, and these women were more likely to be older and have been trying to conceive longer before seeking care. Women who presented first to a generalist provider were less likely to receive IVF (aOR 0.48, 95% CI 0.28, 0.82), were equally likely to achieve pregnancy, and had similar times to pregnancy (aHR 1.11, 95% CI 0.80, 1.53) compared to women who presented first to a subspecialist.
Conclusions
Generalist providers are frequently the first point of care for women with difficulty conceiving and are uniquely positioned to promote a balanced management of infertility.
Keywords: infertility, entry to care, generalist providers, primary care, subspecialty care, in vitro fertilization, time to pregnancy
Introduction
The management of infertility (defined clinically as 12 or more consecutive months of sexual intercourse without contraception and without achieving pregnancy) is part of comprehensive primary care. Fertility care is a fundamental part of the family planning spectrum, involves both women and men, and provides insight into a patient’s overall health, including underlying health problems that increase women’s long-term risk of ischemic heart disease or cancer.1–4 Infertility is common, with prevalence estimates ranging from 7.4% of married women of reproductive age5 to 15.5% of women who are trying to conceive,6,7 and it has major effects on the physical and emotional health of affected women and men.8–11
The frequency of contact and longitudinal relationships in primary care make generalist providers well positioned to assess a woman’s pregnancy intentions and provide guidance to improve the likelihood of achieving a pregnancy and healthy live birth.8,12 While the value of preconception care is well recognized, the role of a primary care provider in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility is not well studied. A better understanding of generalist providers’ role in the diagnosis and treatment of infertility may provide insight into opportunities for enhanced management of infertility in primary care settings.
Using data from a retrospective cohort study, we sought to describe the types of providers women with a history of primary infertility first saw for fertility care and assess any differences in patient characteristics between women who sought initial fertility care from a generalist provider (including family physicians, obstetrician-gynecologists, and midlevel primary care providers), and those who sought initial care from a fertility subspecialist. We also explored the association between the type of provider initially seen for infertility, the likelihood of receiving in vitro fertilization (IVF), and time to pregnancy leading to first live birth.
Methods
We analyzed data from the Fertility Experiences Study (FES), a retrospective cohort study conducted between April 2010 and September 2012. The FES enrolled women with a history of primary infertility, defined as 12 months of intercourse with a man without contraception and without a resulting conception. The primary purpose of the study was to examine time to pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes for different treatment strategies among women with primary infertility.13 This study was approved by the ___ Institutional Review Board (IRB# RB_00027783).
The FES enrolled two parallel cohorts of participants: one from the general population, and one from two participating fertility specialty clinics. Potential participants from the general population were identified using the Utah Population Database, which houses data from Utah birth, death, marriage, and driver license records.14 Potential participants were women married in Utah between January 1, 2000 and December 31, 2002, age 18–30 at time of marriage, and not listed as a mother on a live birth or fetal death certificate as of December 31, 2004 (index date). We mailed letters to a random sample of potential participants inviting them to complete the screening questionnaire. The process was repeated using the same criteria for women married between January 1, 2004 and December 31, 2006, with an index date of December 31, 2008.
We recruited a parallel cohort of clinic-based participants through the two major fertility clinics providing in vitro fertilization (IVF) in Utah at the time of the study: the Utah Center for Reproductive Medicine (UCRM) and Reproductive Care Center (RCC). We mailed recruitment letters to all female patients seen for their first infertility visit at RCC between 2000–2009, and to all female patients seen for their first infertility visit at UCRM in 2004 or 2008 who were age 20–35 at first visit and had no known pregnancies prior to their first visit.
Women who responded to the mailing were screened for eligibility by phone or online. Eligibility criteria for the study were the same for both population-based and clinic-based recruitment from both clinics: age 20–35 at index date, no pregnancies prior to the index date, having been in a sexual relationship with a male for at least one year without contraception and without pregnancy at the time of the index date, and living in Utah for the entire three years following the index date. Upon being found eligible, participants were sent an online (or paper) questionnaire. After completing the questionnaire, participants were contacted to complete a phone interview. Duplicate contacts to the same participant were identified during the screening or data analysis; women who were recruited through both population and clinic cohorts were included in the population cohort. The methods of the Fertility Experiences Study are reported in greater detail elsewhere.13
The written questionnaire and the phone interview included detailed questions regarding treatment choices and outcomes during each period of time during which the woman was attempting to conceive. Our previous validation study found high levels of correlation between patient self-report and medical records for time attempting to conceive (Pearson’s rho=0.61), pregnancy and live birth histories (kappa=0.70), and use of in vitro fertilization (kappa=0.77).15 For each period of time during which a woman was attempting to conceive, interviewers asked, “During this period did you see a doctor or provider specifically for fertility-related issues?” If yes, she was then asked, “Did you meet or consult with:
A general physician/provider (obstetrician, family medicine physician, physician assistant, nurse midwife, nurse practitioner)?
A fertility specialist?
Utah Center for Reproductive Medicine (UCRM)?
Reproductive Care Center (RCC)?
Out of state?
An alternative/holistic practitioner (chiropractor, acupuncturist, naturopath, etc.)?
Other?”
All positive responses were recorded. We classified women’s initial provider according to the first type of provider they saw for fertility care. If a woman indicated that she saw both a generalist provider and a fertility subspecialist during the same period of time, we assumed she saw the generalist provider first. We compared the demographic characteristics of women presenting first to a generalist provider with those of women presenting first to a fertility subspecialist by stratifying the data for each characteristic and calculating the relative risk of presenting to a generalist provider first for each stratum.
Next, we compared the likelihood of receiving IVF among women presenting first to a generalist provider with that of women presenting first to a fertility subspecialist. We included any use of in vitro fertilization (IVF), with or without intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) at any time prior to the woman’s phone interview. We calculated unadjusted odds ratios and conducted a multivariate regression analysis. We considered potential confounders those variables consistent with prior knowledge of factors associated with fertility treatment choices16 and variables that resulted in a greater than 10% difference between the unadjusted and adjusted relative risks of receiving IVF.
We also compared time to pregnancy leading to a live birth by initial provider type, measured from the beginning of the woman’s first attempt to conceive and counting all cumulative months attempting until the beginning of her first pregnancy leading to live birth. We then conducted a multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression model, adjusting for the same potential confounders as in the multivariate regression analysis described above.
We conducted the analysis with Stata statistical software. We analyzed all eligible women in the population and clinic cohorts combined. To assess whether our findings were biased by the half of the sample coming from fertility clinics, we also conducted a secondary analysis including only women recruited from the general population.
Results
Participant Characteristics
In the general population cohort, 16,001 letters were sent, from which 1,903 women (12%) responded with interest, of which 570 women (30%) were eligible, of which 434 (76%) completed the online questionnaire and the telephone interview. Among those recruited through the clinic, there were 10,677 letters sent, 1,303 (12%) interested responses, 526 women (40%) eligible, and 433 (82%) who completed the questionnaire and interview.13 Thus, 867 women were included in the analysis. Participant demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. [Insert Table 1]
Table 1.
Participant characteristics
| Population Cohort | Clinic Cohort | Combined Cohorts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Overall | 434 | – | 433 | – | 867 | – |
| Household income | ||||||
| -Under $12,000 | 8 | 2% | 4 | 1% | 12 | 1% |
| -$12,001 – $25,000 | 20 | 5% | 14 | 3% | 34 | 4% |
| -$25,001 – $50,000 | 129 | 30% | 87 | 20% | 216 | 25% |
| -$50,001 – $75,000 | 159 | 37% | 124 | 29% | 283 | 33% |
| -$75,001 – $100,000 | 67 | 15% | 108 | 25% | 175 | 20% |
| -Over $100,000 | 35 | 8% | 76 | 18% | 111 | 13% |
| -No answer | 16 | 4% | 20 | 5% | 36 | 4% |
| Insurance coverage for infertility testing and/or treatment | ||||||
| -None, unsure, or no answer | 310 | 71% | 358 | 83% | 668 | 77% |
| -Some coverage other than IVF | 111 | 26% | 62 | 14% | 173 | 20% |
| -IVF coverage | 13 | 3% | 13 | 3% | 26 | 3% |
| Religious preference | ||||||
| -None | 38 | 9% | 37 | 9% | 75 | 9% |
| -Latter-day Saint | 343 | 79% | 319 | 74% | 662 | 76% |
| -Catholic | 6 | 1% | 17 | 4% | 23 | 3% |
| -Other Christian | 21 | 5% | 40 | 9% | 61 | 7% |
| -Other non-Christian | 13 | 3% | 10 | 2% | 23 | 3% |
| -No answer | 13 | 3% | 10 | 2% | 23 | 3% |
| Religious attendance | ||||||
| -Never | 58 | 13% | 46 | 11% | 104 | 12% |
| -Monthly or less | 56 | 13% | 63 | 15% | 119 | 14% |
| -Weekly or more | 310 | 71% | 315 | 73% | 625 | 72% |
| -No answer | 10 | 2% | 9 | 2% | 19 | 2% |
| Body mass index | ||||||
| -Under 25 kg/m2 | 194 | 45% | 206 | 48% | 400 | 46% |
| -25–30 kg/m2 | 107 | 25% | 97 | 22% | 204 | 24% |
| -Over 30 kg/m2 | 97 | 22% | 94 | 22% | 191 | 22% |
| -No answer | 36 | 8% | 36 | 8% | 72 | 8% |
| Age at beginning of first attempt to conceive | ||||||
| -Under 25 years | 274 | 63% | 201 | 46% | 475 | 55% |
| -25–30 years | 141 | 32% | 161 | 37% | 302 | 35% |
| -Over 30 years | 19 | 4% | 67 | 15% | 86 | 10% |
| -No answer | 0 | 0% | 4 | 1% | 4 | 0% |
| Age at first infertility visit | ||||||
| -Under 25 years | 151 | 35% | 145 | 33% | 296 | 34% |
| -25–30 years | 173 | 40% | 168 | 39% | 341 | 39% |
| -Over 30 years | 35 | 8% | 112 | 26% | 147 | 17% |
| -Not applicable or no answer | 75 | 17% | 8 | 2% | 83 | 10% |
| Cumulative months attempting to conceive before first infertility visit | ||||||
| -11 months or less | 125 | 29% | 156 | 36% | 281 | 32% |
| -12–23 months | 156 | 36% | 190 | 44% | 346 | 40% |
| -24–35 months | 47 | 11% | 41 | 9% | 88 | 10% |
| -Over 36 months | 31 | 7% | 42 | 10% | 73 | 8% |
| -Not applicable or no answer | 75 | 17% | 4 | 1% | 79 | 9% |
First Provider Type for Infertility Care
Among all 867 study participants, a majority (84%) presented first to a generalist provider for fertility care. Only 8% presented first to a fertility subspecialist, and 8% never saw any type of provider specifically for fertility care despite failing to achieve a pregnancy after being in a sexual relationship with a male without use of contraceptives for at least one year. Women were equally likely to achieve a live birth regardless of first provider type (chi-squared p=0.39). Figure 1 displays the number of women in each category who had a live birth. This analysis was repeated for the 434 women recruited from population sampling alone, with similar results shown in Supplemental Figure 1. [Insert Figure 1]
Figure 1.
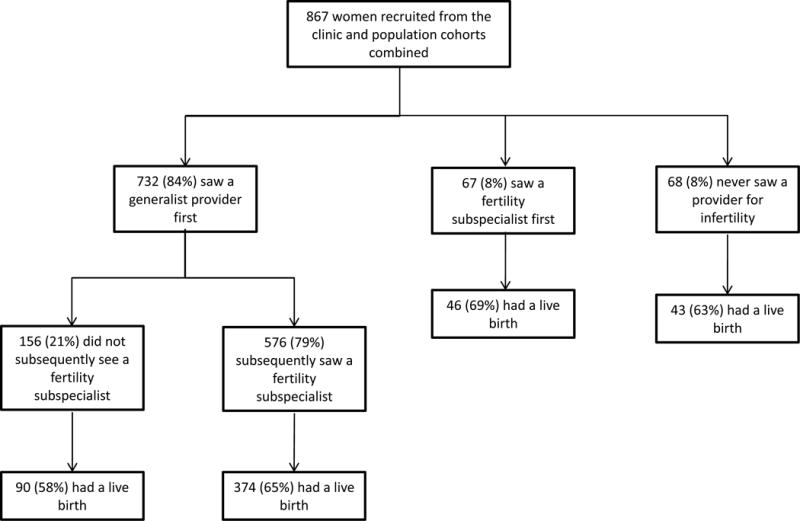
Provider types and outcomes
Women who entered care with subspecialists were older at the beginning of their first attempt to conceive, were older at the time of their first fertility visit, and had been trying longer to conceive at the time of their first fertility visit, as shown in Table 2. [Insert Table 2] These results were were not statistically significant when restricted to women recruited from population sampling alone, as shown in Supplemental Table 1.
Table 2.
Association between select characteristics and likelihood of seeing a fertility subspecialist first
| General Provider First | Fertility Specialist First | Relative Risk of Seeing a Fertility Specialist First (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Overall | 732 | 92% | 67 | 8% | – |
| Recruitment method | |||||
| -General population | 346 | 94% | 22 | 6% | ref. |
| -Fertility clinic | 386 | 90% | 45 | 10% | 1.74 (1.07, 2.85) |
| Household income | |||||
| -$50,000 or less | 218 | 94% | 14 | 6% | ref. |
| -$50,001 – $75,000 | 241 | 92% | 21 | 8% | 1.32 (0.69, 2.55) |
| -Over $75,000 | 243 | 90% | 28 | 10% | 1.71 (0.92, 3.17) |
| Insurance coverage for infertility testing and/or treatment | |||||
| -None or unsure | 546 | 91% | 54 | 9% | ref. |
| -Some coverage other than IVF | 161 | 93% | 12 | 7% | 0.77 (0.42, (1.41) |
| -IVF coverage | 25 | 96% | 1 | 4% | 0.43 (0.06, 2.97) |
| Religious preference | |||||
| -None | 56 | 88% | 8 | 13% | ref. |
| -Latter-day Saint | 570 | 92% | 47 | 8% | 0.61 (0.30, 1.23) |
| -Other than Latter-day Saint | 86 | 89% | 11 | 11% | 0.91 (0.39, 2.13) |
| Religious attendance | |||||
| -Never | 83 | 90% | 9 | 10% | ref. |
| -Monthly or less | 95 | 92% | 8 | 8% | 0.79 (0.32, 1.97) |
| -Weekly or more | 537 | 92% | 49 | 8% | 0.85 (0.43, 1.68) |
| Body mass index | |||||
| -Under 25 kg/m2 | 337 | 91% | 32 | 9% | ref. |
| -25–30 kg/m2 | 176 | 93% | 13 | 7% | 0.79 (0.43, 1.47) |
| -Over 30 kg/m2 | 159 | 91% | 16 | 9% | 1.05 (0.59, 1.87) |
| Age at beginning of first attempt to conceive | |||||
| -Under 25 years | 406 | 93% | 29 | 7% | ref. |
| -25–30 years | 251 | 91% | 26 | 9% | 1.41 (0.85, 2.34) |
| -Over 30 years | 71 | 86% | 12 | 14% | 2.17 (1.15, 4.07) |
| Age at first infertility visit | |||||
| -Under 25 years | 279 | 94% | 17 | 6% | ref. |
| -25–30 years | 316 | 93% | 25 | 7% | 1.27 (0.70, 2.32) |
| -Over 30 years | 123 | 84% | 24 | 16% | 2.84 (1.58, 5.12) |
| Cumulative months attempting to conceive before first infertility visit | |||||
| -11 months or less | 266 | 95% | 15 | 5% | ref. |
| -12–23 months | 311 | 90% | 35 | 10% | 1.89 (1.06, 3.39) |
| -24 months or longer | 145 | 90% | 16 | 10% | 1.86 (0.95, 3.66) |
Likelihood of Receiving In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Women who presented first to generalist providers were less likely to receive IVF than women who presented first to fertility subspecialists (OR 0.42, 95% CI 0.26, 0.70). This remained significant after adjusting for household income, age at time of first fertility visit, and length of time trying to conceive at time of first fertility visit (aOR 0.48, 95% CI 0.28, 0.82). In the analysis limited to women recruited from the population-based sample, women were similarly less likely to receive IVF (OR 0.24, 95% CI 0.10, 0.59); this finding remained significant after the same multivariate adjustment (aOR 0.25, 95% CI 0.10, 0.63).
Time to Pregnancy
Among the 553 women who had a live birth, median time to pregnancy ending in live birth was 35 months for women who first visited a generalist provider, and 31 months for women who first visited a subspecialist (rank-sum test p=0.97). 51.2% of women who initiated care with a generalist provider achieved pregnancy within the first 5 years of attempting, compared with 50.7% for women who initiated care with a subspecialist (chi2 p=0.94). Figure 2 shows the time to pregnancy leading to live birth by first provider type. [Insert Figure 2]
Figure 2.
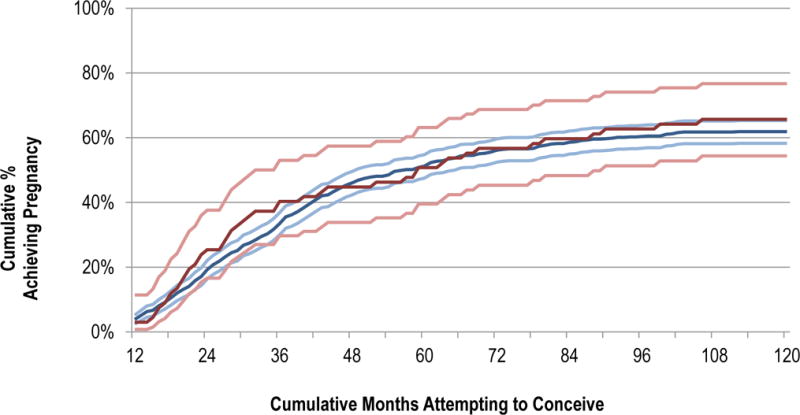
Time to pregnancy leading to live birth.

There was no statistically significant difference in time to pregnancy between women who presented first to a generalist provider and women who presented first to a fertility subspecialist based on a comparison of hazard ratios (combined cohorts: HR 0.93, 95% CI 0.69, 1.27; population cohort only: HR 1.00, 95% CI 0.57, 1.76). This remained the case after adjusting for household income, age at time of first fertility visit, and length of time trying to conceive at time of first fertility visit (combined cohorts: aHR 0.94, 95% CI 0.68, 1.30; population cohort only: aHR 1.08, 95% CI 0.60, 1.94).
Discussion
The first point of contact for most women seeking fertility care in this population was a generalist provider. Presenting first to a generalist provider was associated with a decreased likelihood of receiving IVF and a similar time to pregnancy leading to first live birth. These findings do not necessarily imply a causal relationship between first provider type and likelihood of receiving IVF. Women who seek infertility care from different types of providers likely differ beyond the factors we measured, such as etiology of infertility. Further research is needed to determine the underlying reasons for the association detected in this study.
Specialized fertility treatments such as IVF can be medically invasive and are associated with a number of adverse health implications for resulting children, including an increased risk of birth defects, low birth weight, and preterm birth.8,17–19 They are also more costly. If similar live birth outcomes can be achieved with lower rates of IVF utilization, it may be beneficial for both patients and society.20
This study’s strengths include its use of data from population-based participants, rather than clinic-based participants only, increasing its ability to represent the general population and the population that generalist providers see in practice. Other strengths include a moderately large sample size, inclusion of all (two) subspecialty fertility clinics in the state of Utah at the time of the study, collection of detailed time-related data for attempts to conceive and pregnancy outcomes, and the use of a validated questionnaire for assessing fertility treatments and time to conception.
Several limitations should be noted. First, the questionnaire did not differentiate between various types of generalist providers; instead, family physicians, obstetrician-gynecologists, physician assistants, and nurse practitioners were combined into one category. Experience and training for infertility may vary considerably among these different types of providers. Second, the questionnaire relied on participants to classify their provider type as a generalist provider or a fertility specialist. As a result, it is possible that some obstetrics-gynecology clinics that advertise a focus on infertility may have been misclassified as fertility subspecialists, which for the purpose of this study are defined as reproductive endocrinologists. Third, several unique characteristics of the women in this study and in the Utah population may limit generalizability to other populations. The Utah population has higher fertility among women and a younger average age at childbearing (23.9 years at first birth in Utah, vs. 25 years nationally).21 In addition, 76% of women in this study self-identified as Latter-day Saint (LDS), and the pronatalist stance of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints may influence women’s experience and treatment decisions.21,22 We believe it is unlikely that this cultural influence would change the impact of generalist versus specialist care initially for women under 35 years of age. Finally, we have previously reported that women who responded to the original recruitment letter were somewhat more likely than nonresponders to have had a live birth, be older (in the clinic group), and more educated (in the population group).13 It is theoretically possible that the relationship between time to pregnancy and type of first provider could be different among the nonresponders who would have been eligible for the study.
This study highlights the importance of primary care and generalist providers in the treatment of infertility. Infertility is relatively common, and the majority of women in our study sought medical care for this condition. Further, a large majority of women who sought care presented first to a generalist provider. Many generalist providers may perceive infertility as a relatively infrequent complaint despite their being the initial source of advice for patients with this condition.23 There may be some discrepancy between patients’ and providers’ perceptions of what constitutes seeking infertility care, and this may contribute to some patients feeling as though their fertility concerns are not taken seriously by generalist providers.24 Despite its high prevalence, infertility may be an infrequently addressed topic in family medicine residencies and other primary care training programs.
A greater comprehensiveness of care among family physicians has been associated with lower costs.25 Generalist providers who perform the initial workup and management of infertility may confer cost savings on their patients and on the health care system. They may also improve patient access to infertility care, especially for patients who, as a result of health care reform efforts, may now have increased access to primary care without increased access to subspecialty infertility care. Generalist providers are uniquely positioned to promote a balanced management of infertility and may help some patients avoid unnecessary medical complications, cost, and stress associated with invasive fertility treatments.
Suggestions for further research include studies comparing the outcomes of fertility care provided by various types of generalist providers and fertility subspecialists among samples representative of the U.S. population, the current and potential economic impact of fertility care by generalist providers, generalist providers’ perspectives and self-perceived readiness to provide fertility care, and patient satisfaction of fertility care by various provider types.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Partial support for all datasets within the Utah Population Database was provided by the University of Utah Huntsman Cancer Institute and the Huntsman Cancer Institute Cancer Center Support grant, P30 CA2014 from the National Cancer Institute.
Funding Statement:
The Fertility Experiences Study was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, R21 HD060213-01A1, and a grant from the Primary Children’s Medical Center Foundation, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Footnotes
Conflicting or Competing Interests:
The authors have no conflicting or competing interests to declare.
Prior Presentations:
Portions of the findings reported here have been presented at the following conferences: American Association of Family Physicians National Conference of Family Medicine Residents and Medical Students, 2015, Kansas City, MO; Society of Teachers of Family Medicine Conference on Medical Student Education, 2016, Phoenix, AZ
Note to NIH – Please include: The published version of this article can be accessed for free on the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine website at: http://jabfm.org/content/30/2/230.full
References
- 1.Dahlgren E, Janson PO, Johansson S, Lapidus L, Oden A. Polycystic ovary syndrome and risk for myocardial infarction. Evaluated from a risk factor model based on a prospective population study of women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1992;71(8):599–604. doi: 10.3109/00016349209006227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brinton LA, Westhoff CL, Scoccia B, et al. Causes of infertility as predictors of subsequent cancer risk. Epidemiology. 2005;16(4):500–507. doi: 10.1097/01.ede.0000164812.02181.d5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Simonsen SE, Baksh L, Stanford JB. Infertility treatment in a population-based sample: 2004–2005. Matern Child Health J. 2012;16(4):877–886. doi: 10.1007/s10995-011-0809-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vannuccini S, Clifton VL, Fraser IS, et al. Infertility and reproductive disorders: impact of hormonal and inflammatory mechanisms on pregnancy outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 2016;22(1):104–115. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chandra A, Martinez GM, Mosher WD, Abma JC, Jones J. Fertility, family planning, and reproductive health of U.S. women: data from the 2002 National Survey of Family Growth. Vital Health Stat. 2005;23(25):1–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stanford JB. What is the true prevalence of infertility? Fertil Steril. 2013;99(5):1201–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thoma ME, McLain AC, Louis JF, et al. Prevalence of infertility in the United States as estimated by the current duration approach and a traditional constructed approach. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(5):1324–1331 e1321. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.11.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Public Health Action Plan for the Detection P, and Management of Infertility. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2014. J. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, de Mouzon J, et al. International Committee for Monitoring Assisted Reproductive Technology (ICMART) and the World Health Organization (WHO) revised glossary of ART terminology, 2009. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(5):1520–1524. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Greil AL, Shreffler KM, Schmidt L, McQuillan J. Variation in distress among women with infertility: evidence from a population-based sample. Human Reproduction. 2011;26(8):2101–2112. doi: 10.1093/humrep/der148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pook M, Krause W, Rohrle B. Coping with infertility: distress and changes in sperm quality. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(6):1487–1492. doi: 10.1093/humrep/14.6.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dunlop AL, Jack BW, Bottalico JN, et al. The clinical content of preconception care: women with chronic medical conditions. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;199(6 Suppl 2):S310–327. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2008.08.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stanford JB, Sanders JN, Simonsen SE, Hammoud A, Gibson M, Smith KR. Methods for a Retrospective Population-based and Clinic-based Subfertility Cohort Study: the Fertility Experiences Study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2016 doi: 10.1111/ppe.12291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.DuVall SL, Fraser AM, Rowe K, Thomas A, Mineau GP. Evaluation of record linkage between a large healthcare provider and the Utah Population Database. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association: JAMIA. 2012;19(e1):e54–59. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2011-000335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Thomas FS, Stanford JB, Sanders JN, et al. Development and initial validation of a fertility experiences questionnaire. Reprod Health. 2015;12:62. doi: 10.1186/s12978-015-0054-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chandra A, Copen CE, Stephen EH. Infertility service use in the United States: data from the National Survey of Family Growth, 1982–2010. Natl Health Stat Report. 2014;73:1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Davies MJ, Moore VM, Willson KJ, et al. Reproductive technologies and the risk of birth defects. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(19):1803–1813. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1008095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schieve LA, Rasmussen SA, Buck GM, Schendel DE, Reynolds MA, Wright VC. Are children born after assisted reproductive technology at increased risk for adverse health outcomes? Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103(6):1154–1163. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000124571.04890.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Okun N, Sierra S, Canada SoOaGo Pregnancy outcomes after assisted human reproduction. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2014;36(1):64–83. doi: 10.1016/S1701-2163(15)30685-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Stanford JB, Mikolajczyk RT, Lynch CD, Simonsen SE. Cumulative pregnancy probabilities among couples with subfertility: effects of varying treatments. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(7):2175–2181. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sanders J, Simonsen S, Porucznik CA, Baksh L, Stanford JB. Use of fertility treatments in relation to the duration of pregnancy attempt among women who were trying to become pregnant and experienced a live birth. Matern Child Health J. 2014;18(1):258–267. doi: 10.1007/s10995-013-1262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stanford JB, Smith KR. Marital fertility and income: moderating effects of the church of jesus christ of latter-day saints religion in utah. J Biosoc Sci. 2013;45(2):239–248. doi: 10.1017/S002193201200065X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wilkes S, Hall N, Crosland A, Murdoch A, Rubin G. General practitioners’ perceptions and attitudes to infertility management in primary care: focus group study. J Eval Clin Pract. 2007;13(3):358–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2006.00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hinton L, Kurinczuk JJ, Ziebland S. Reassured or fobbed off? Perspectives on infertility consultations in primary care: a qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract. 2012;62(599):e438–445. doi: 10.3399/bjgp12X649133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bazemore A, Petterson S, Peterson LE, Phillips RL. More Comprehensive Care Among Family Physicians is Associated with Lower Costs and Fewer Hospitalizations. Ann Fam Med. 2015;13(3):206–213. doi: 10.1370/afm.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


