Figure 1.
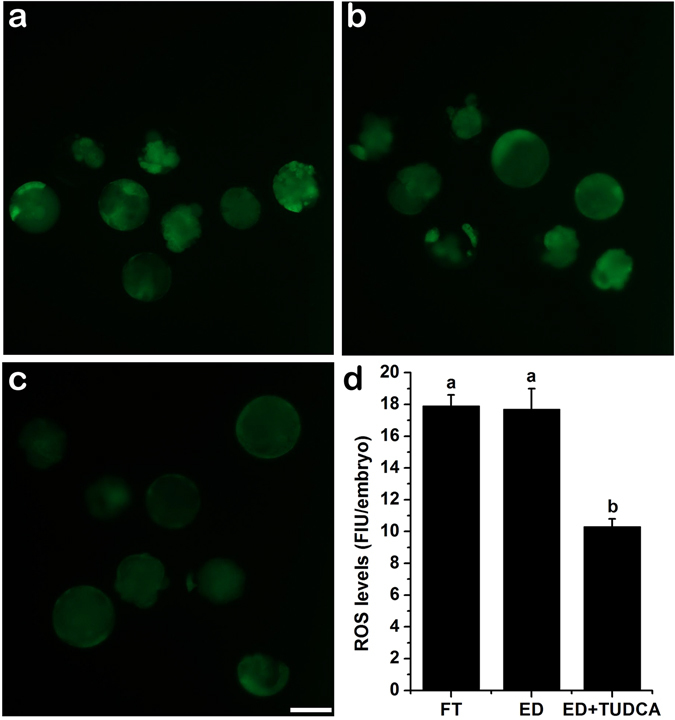
Effect of TUDCA supplementation during embryo culture on the levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in porcine blastocysts. Representative fluorescence images of blastocysts from in vitro matured oocytes fertilized using ICSI with the conventional freeze-thaw (FT) boar spermatozoa without TUDCA-treatment (a), evaporatively dried boar spermatozoa without TUDCA-treatment (b) or evaporatively dried boar spermatozoa with 200 μM TUDCA-treatment (c). Bar: 100 μm. d. ROS contents were quantified as fluorescent intensity for three independent times. Each time 6–12 blastocysts were measured. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of the fluorescent density. Bars that do not share the same letter are significantly different at p < 0.05.
