Fig. 1.
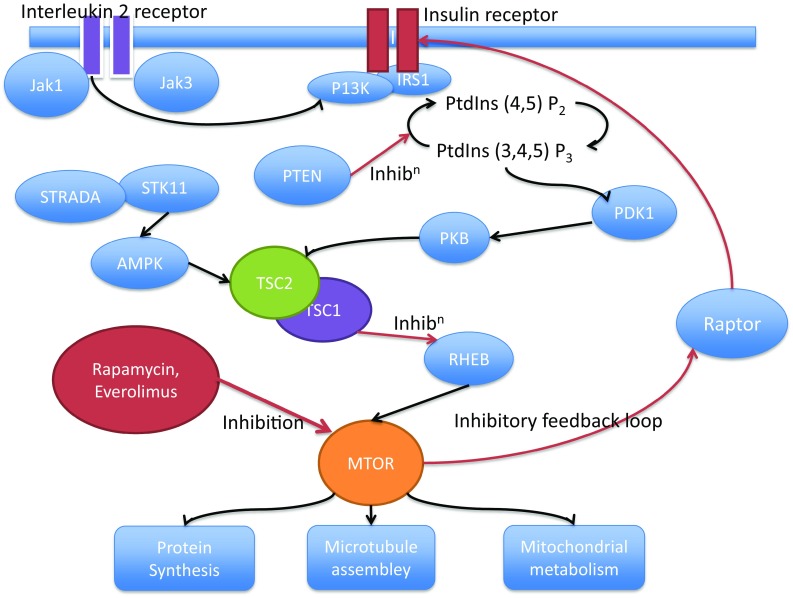
Pathway showing some of the relationships between mTOR and cellular function which may be modulated in epileptogenesis and their modulation through inflammatory pathways and by drugs. AMPK 5′ AMP-activated protein kinase, IRS1 insulin receptor substrate 1, JAK Janus kinase, MTOR mechanistic target of rapamycin, PDK1 pyruvate dehydrogenase lipoamide kinase isozyme 1, P13K PI3 kinase, PKB protein kinase B, PtdIns phosphatidylinositol, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homologue, RHEB ras homolog enriched in brain (GTP binding protein), STRADA STE20-related kinase adaptor alpha, STK11 serine/threonine kinase 11, TSC tuberous sclerosis complex
