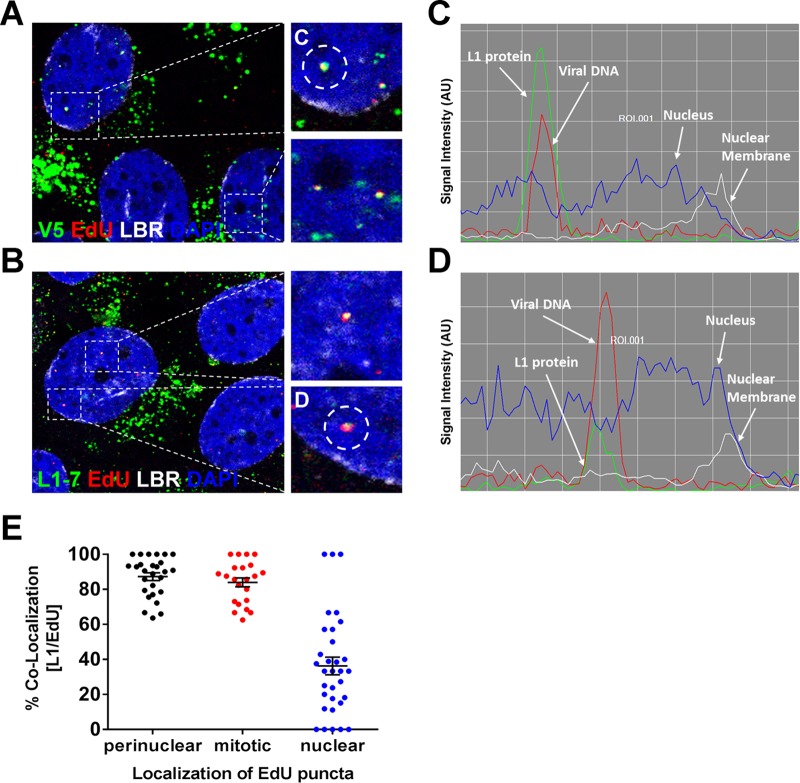
FIG 5.
L1 protein accompanies the viral genome into the nucleus. (A) At 24 hpi, HaCaT cells infected with EdU-labeled pseudovirus were fixed and permeabilized. Next, the cells were incubated with L1 conformationally dependent mouse MAb H16.V5 antibody (green) and rabbit pAb anti-lamin B receptor (LBR) (white). Lastly, the cells were treated with Click-iT reaction buffer with AF555 dye (red) to stain EdU-labeled pseudogenome and mounted in DAPI (blue). (B) At 24 hpi, HaCaT cells infected with EdU-labeled pseudovirus were fixed, permeabilized, and treated with Click-iT reaction buffer without dye. Next, cells were incubated with mouse MAb 33L1-7 antibody (green) and rabbit pAb anti-LBR (white). Lastly, the cells were treated with Click-iT reaction buffer with AF555 dye (red) to stain EdU-labeled pseudogenome and mounted in DAPI (blue). (C and D) Colocalization of L1 and EdU puncta within the nucleus was assessed by acquiring Z-stack images of infected cells. The signal intensities of single puncta were assessed by analyzing the line profile of individual EdU puncta. Note that the signal intensity is expressed in arbitrary units (AU). (E) Quantifications are from two repeat experiments analyzing single slice images of Z-stacks (n = 25 to 30 cells, and >800 EdU puncta were counted). Data are reported as percentages of the colocalization between L1 and EdU puncta as a function of the EdU localization within the cell. Puncta: perinuclear localized EdU puncta within interphase cells = 87.3% ± 2.2%; condensed chromatin-associated EdU puncta within mitotic cells = 84.0% ± 2.6%; and nuclear localized EdU puncta within interphase cells = 36.3% ± 5.1%.