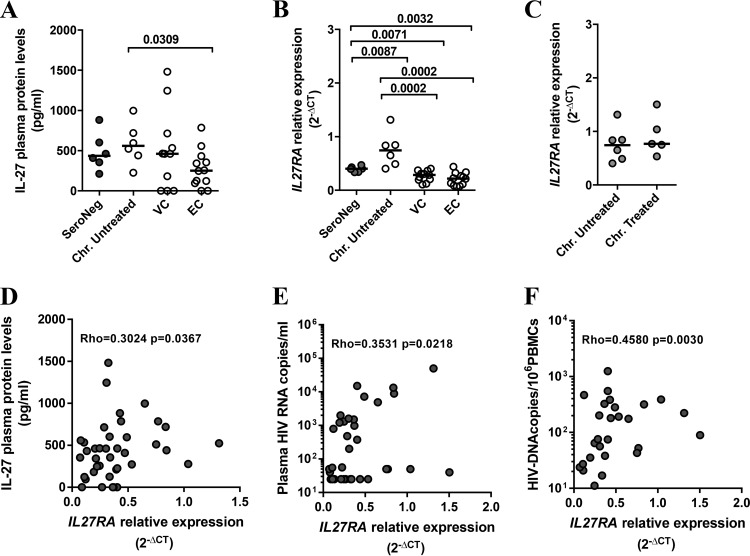
FIG 4.
Low IL-27/IL27RA plasma levels during HIV chronic infection are associated with viral control. (A) Differential plasma levels of IL-27 detected by ELISA (picograms/milliliter) are shown for samples from validation cohorts, including HIV seronegatives (SeroNeg) (n = 6), chronically infected, viremic, untreated HIV-infected individuals (Chr. Untreated) (n = 6), HIV viremic controller subjects (VC; n = 11), and HIV elite controller patients (EC; n = 12). (B) HIV seronegatives (n = 6), chronically infected, viremic, untreated HIV-infected individuals (n = 6), HIV viremic controller subjects (VC; n = 11), and HIV elite controller patients (EC; n = 12). (C) Relative expression levels of IL27RA detected in PBMC by RT-PCR in chronically viremic infected subjects. Untreated, n = 6; treated, n = 5. (D to F) Correlation between IL27RA gene expression in PBMC (x axis) and plasma levels of IL-27 (y axis) (D), plasma viral loads (E), and proviral DNA copy number in total PBMC (F) in validation cohorts. The Mann-Whitney test was applied for groups comparisons and Spearman rank test for correlation studies. P values of <0.05 were considered significant.