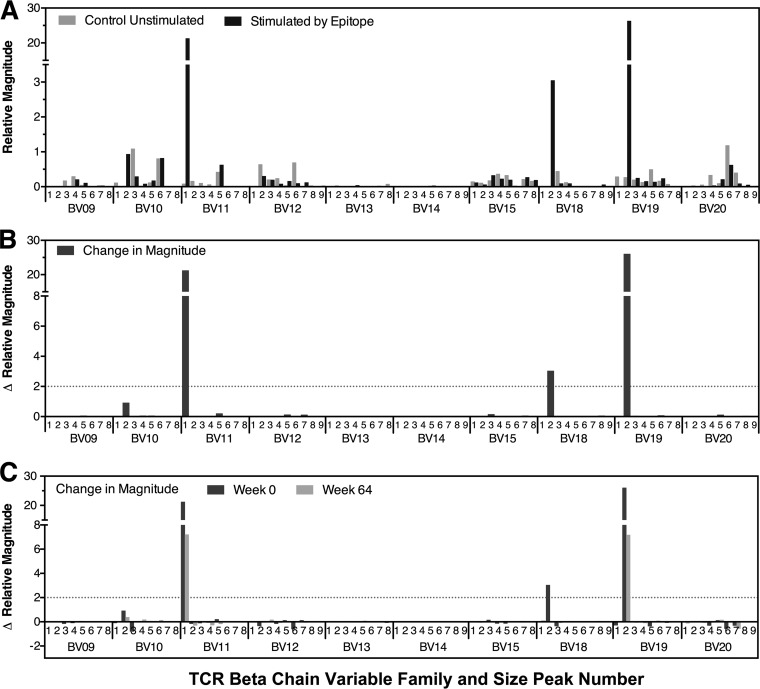
FIG 1.
Delineation of the clonal profile of CTL responses targeting HIV-1 epitopes. An example of quantitative spectratyping is shown. PBMCs were cultured in the presence or absence of the epitope of interest, followed by spectratyping of 24 BV gene families within isolated CD8+ T lymphocytes, using quantitative PCR to determine the copy numbers of each family. The relative concentration of each BV family was calculated as the ratio of its copy number to the median copy number across all families. The relative magnitude of each spectratype peak was calculated as the fraction of the peak area within the summed area of all peaks in its family multiplied by the relative concentration of the family. The last 10 of the 24 analyzed families are shown as representative examples, because they contained a mixture of families with and without epitope-specific responses. (A) Results are shown for unstimulated and peptide-stimulated peak profiles, demonstrating some families with epitope-specific expansions (BV11, BV18, and BV19). (B) The magnitude of change of each peak in response to epitope stimulation was calculated by subtracting the relative magnitude of unstimulated spectratypes from that of epitope-stimulated spectratypes. Results for the same 10 BV families are shown, quantifying the epitope-specific expansions (defined as increases of ≥2 units) in families BV11, BV18, and BV19 from panel A. (C) Results for the magnitude changes of each peak in response to epitope stimulation for the same 10 BV families for two different time points.