Figure 4.
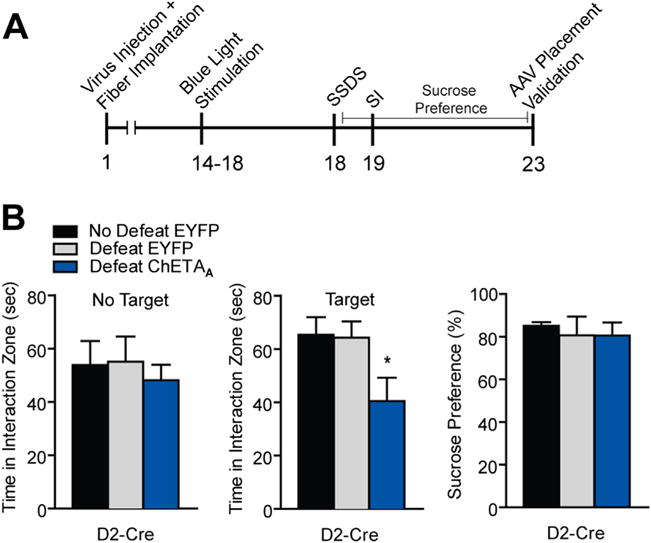
Repeated activation of dopamine receptor D2-medium spiny neurons (MSNs) in stress naïve mice induces susceptibility to subthreshold social defeat stress (SSDS). (A) Experimental timeline of D2-Cre optogenetic stimulation and SSDS. (B) D2-Cre mice receiving repeated priming 50-Hz blue light pulses to nucleus accumbens (NAc) before SSDS and during SSDS displayed reduced social interaction (SI) (one-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] F2,28 = 3.75, p < .05, n = 6–8 animals per group) with no alteration in no target interaction (one-way ANOVA F2,28 = .26, p > .05). Sucrose preference was unaltered in these conditions (one-way ANOVA F2,13 = .10, p > .05). Groups were compared with no defeat enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP) group using a Bonferroni post hoc test: *p < .05. Error bars represent SEM. AAV, adeno-associated virus.
