Figure 5.
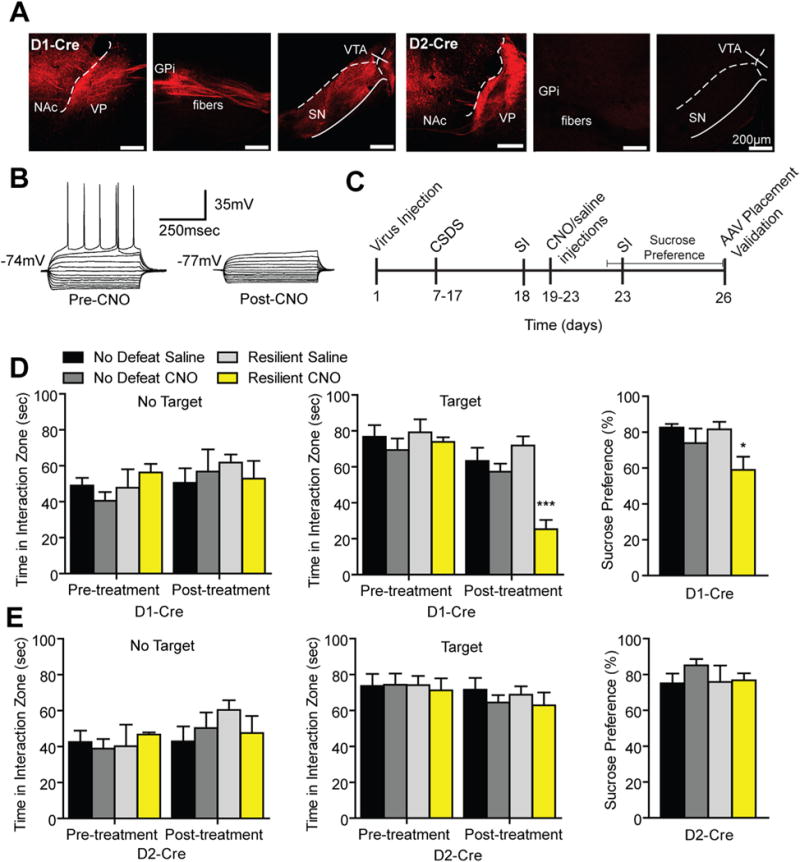
Repeated pharmacogenetic inhibition of dopamine receptor D1-medium spiny neurons (MSNs) but not dopamine receptor D2-MSNs induces a prodepressive phenotype. (A) Experimental timeline of chronic social defeat stress (CSDS) and repeated pharmacogenetic inhibition of D1-Cre and D2-Cre mice. (B) Sagittal confocal images of hM4(Gi)-mCherry expression D1-MSNs and D2-MSNs in the nucleus accumbens (NAc). hM4(Gi) expressing D1-MSNs project to ventral pallidum (VP), globus pallidus internal (GPi), ventral tegmental area (VTA), and substantia nigra (SN) and D2-MSNs project to VP (scale bar 200 μm). (C) Representative traces from a current clamp slice recording of an MSN expressing the hM4(Gi) receptor. A decrease in spiking and input resistance was observed 1 hour following clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) wash on. (D) In resilient D1-Cre mice, repeated CNO injections reduced social interaction (SI) time (two-way repeated measures analysis of variance [ANOVA] significant interaction F3,21 = 5.40, p < .01 with a main effect of treatment F3,21 = 6.354, p < .01; n = 4–8 animals per group) and decreased sucrose preference (two-way ANOVA significant interaction F1,21 = 11.19, p < .01 with a main effect of treatment F1,21 = 11.65, p < .01) without altering interaction zone times without the target present (two-way repeated measures ANOVA nonsignificant interaction F3,21 = 1.13, p > .05). (E) No effects were observed in time spent in the interaction zone with the target or no target (two-way repeated measures ANOVA nonsignificant interaction: target F3,15 = .26, p > .05; no target F3,15 = 1.28, p > .05) or in sucrose preference (two-way ANOVA nonsignificant interaction F1,15 = .52, p > .05) in resilient D2-Cre mice. Groups were compared with no defeat saline group using a Bonferroni post hoc test: *p < .05, ***p < .001. Error bars represent SEM. AAV, adeno-associated virus.
