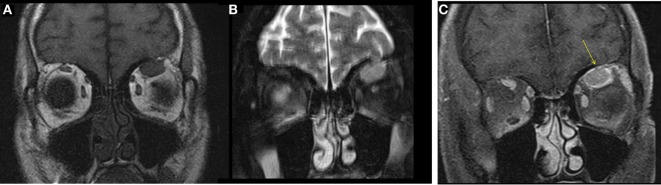
Figure 2.
Case 2. T1 hypointense and T2 hyperintense mildly enhancing mass in the left superior rectus muscle seen on coronal T1 (A), fat saturated T2 (B), and post contrast fat saturated T1 (C) images of the orbits. Solitary muscle involvement especially of the superior rectus makes thyroid orbitopathy an unlikely etiology.