FIGURE 1.
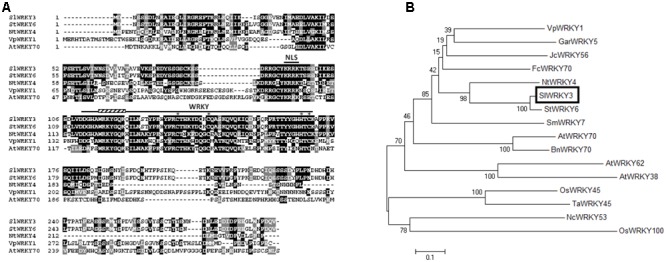
Identification of SlWRKY3. (A) Comparison of SlWRKY3 sequence with StWRKY6, NtWRKY4, VpWRKY1, and AtWRKY70. Identical residues are colored in black, and conserved residues in dark gray. The WRKY domain and the putative nuclear localization site are labeled. The Cys and His residues forming the zinc-finger motif are indicated by stars. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of SlWRKY3 and related proteins: StWRKY6, NtWRKY4, GarWRKY5, JcWRKY56, FcWRKY70, SmWRKY7, VpWRKY1, AtWRKY70, AtWRKY62 and AtWRKY38, NcWRKY53, BnWRKY70, OsWRKY45, OsWRKY100, and TaWRKY45. The phylogenetic tree was constructed according to the neighbor-joining method, using MEGA6 (Tamura et al., 2013). The percentage of reliability of each branch point of the rooted tree, as assessed by the analysis of 1000 trees (bootstrap replicates), is shown on the branch stem.
