Figure 1.
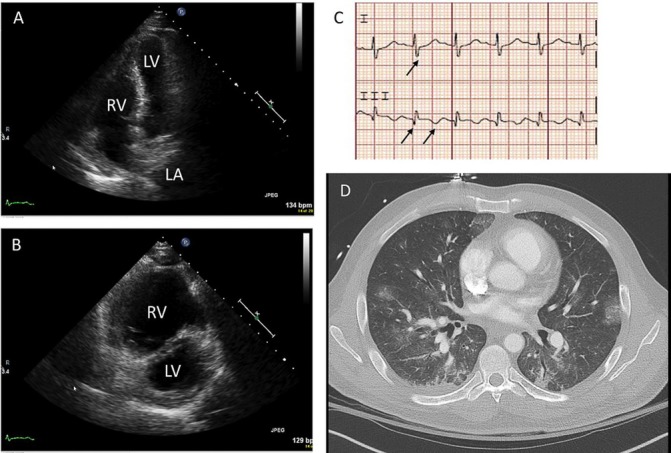
(A) Transthoracic echocardiography, apical four chamber view illustrating bowing of the interventricular septum towards the left ventricle during diastole. (B) Transthoracic echocardiography, parasternal short-axis view with massive RV and septal flattening (‘D-sign’). (C) ECG with S wave in lead I, Q wave and inverted T wave in lead III. (D) CT angiography shows right heart strain with septal flattening and reflux of contrast into IVC, lack of new pulmonary emboli and scattered ground glass infiltrates in the lung bases, concerning for pulmonary haemorrhage. LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle; IVC, inferior vean cava.
