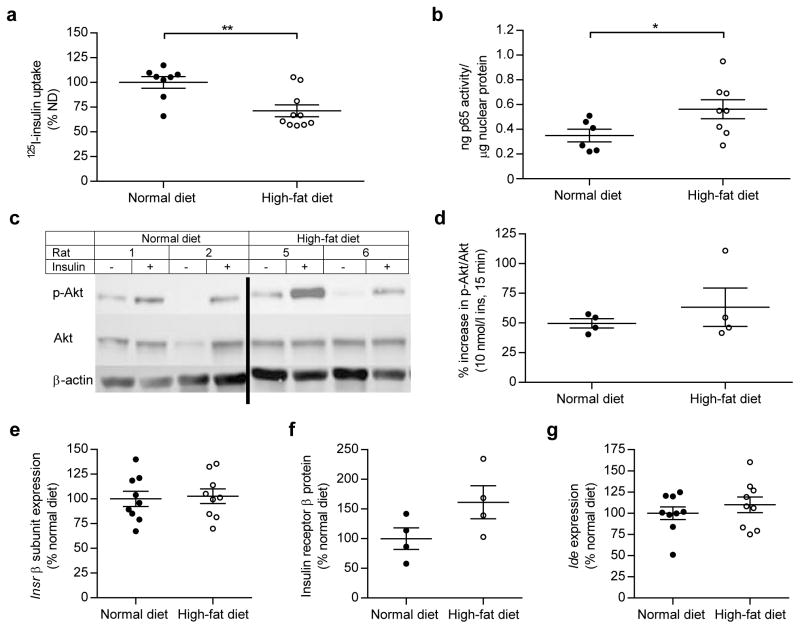
Fig. 3.
HFD feeding decreases insulin uptake and increases NF-κB nuclear binding activity in iBECs despite intact IR expression and signalling. HFD feeding decreased 125I-TyrA14-insulin (125I-insulin) uptake (a) and increased NF-κB nuclear binding activity (b) in iBECs. Representative blot (line denotes crop) (c) and quantification (d) of insulin-stimulated (10 nmol/l, 15 min) Akt phosphorylation (p-Akt, normalised to total Akt) did not differ between ND and HFD rats. IR-β (e, f) and Ide expression (g) did not differ between diet groups. White circles, rats fed an HFD for 4 weeks; black circles, rats fed an ND for 4 weeks. Mann–Whitney U test (a, b), Welch’s t test for non-equal variance (d) and t tests (e, f, g) were used to analyse data. Data presented are means ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01