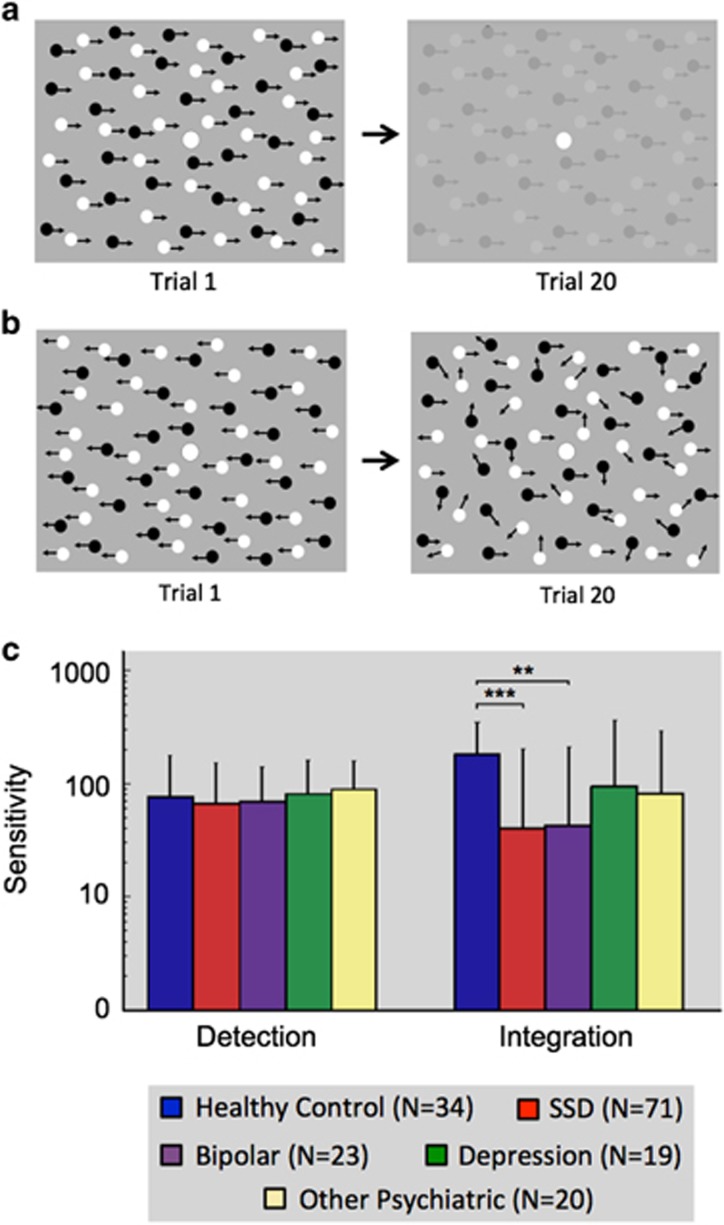
Figure 1.
(a) Stimuli used for the visual detection and (b) integration task. In both instances, the participants reported whether the dots appeared to move to the left or right. Task difficulty was increased by either reducing the black/white contrast relative to the gray background (detection) or the ratio of coherent versus randomly moving dots (integration). (c) Mean sensitivity for different diagnostic groups across visual tasks. The results show no difference between groups in the detection task but significant impairment in integration for both the schizophrenia spectrum disorder (SSD; ***P<0.001) and bipolar (**P<0.01) patients relative to healthy controls. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.