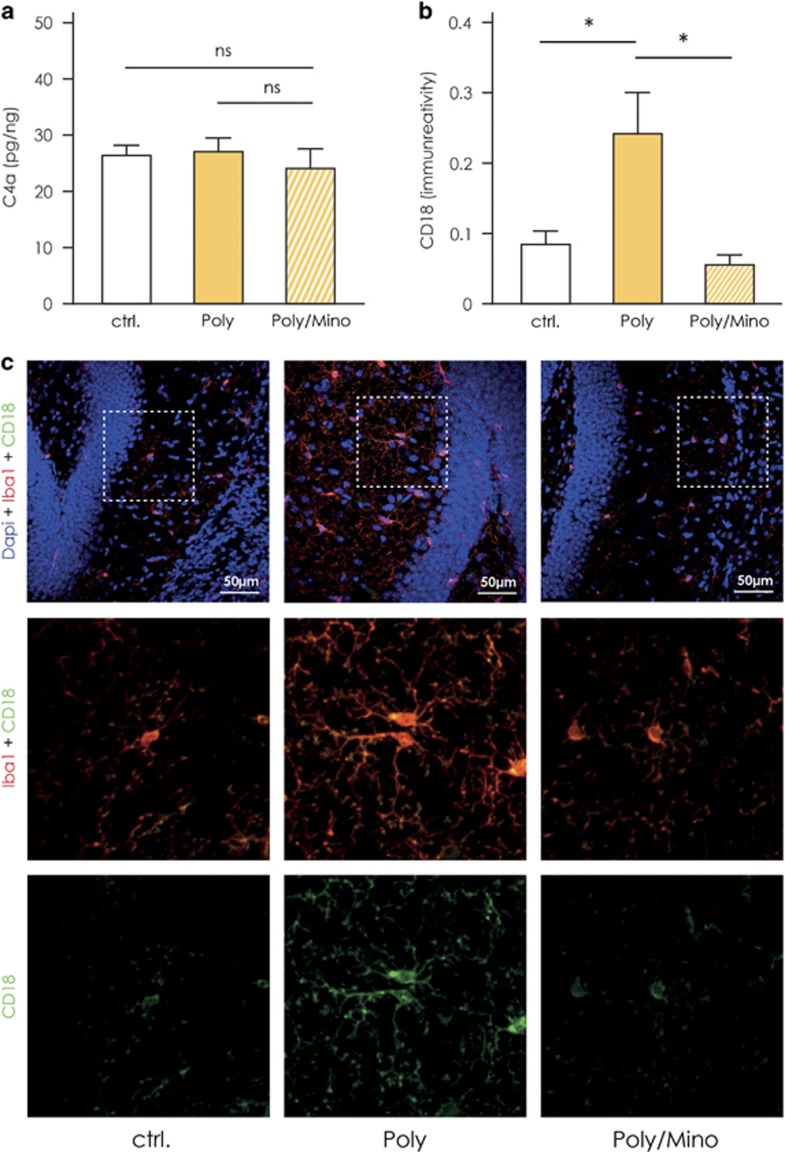
Figure 5.
Changes in the complement system in the hippocampus of Poly(I:C) mice. (a) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) measurement of the complement component 4a (C4a) in whole hippocampal homogenates from Poly(I:C) (n=5), control (n=5) and minocycline-treated Poly(I:C) animals (n=4). No significant difference in C4a levels was detected between the groups. (b) Immunoreactivity for CD18 on microglia measured through the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus (DG) of Poly(I:C) (n=7), controls (n=5) and minocycline-treated Poly(I:C) mice (n=4). CD18 immunoreactivity in Iba1-positive cells was significantly increased in the DG of Poly(I:C) animals as compared with controls and minocycline-treated Poly(I:C) mice. (c) Representative pictures showing the CD18 signal co-localizing with Iba1-positive cells (microglia) and showing the increased CD18 immunoreactivity in the proximity of the DG in Poly(I:C) animals as compared with controls and minocycline-treated Poly(I:C) mice. Error bars represent s.e.m. in all the panels. The data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc test; *P<0.05; ctrl, control animals; NS, not significant; Poly, Poly(I:C) animals; Poly/Mino, Poly(I:C) animals treated with minocycline.