Figure 3.
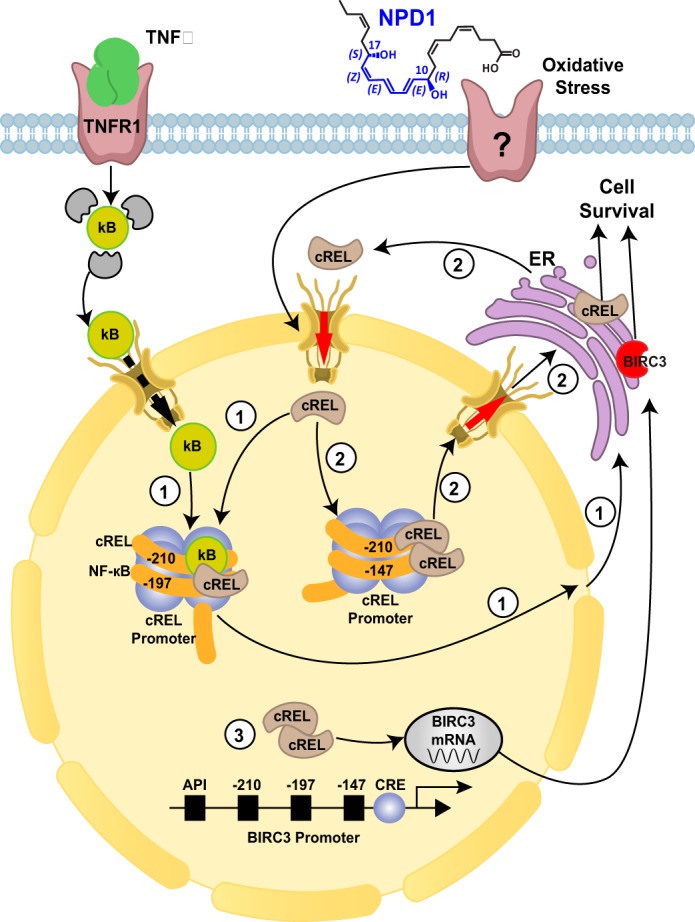
Transcriptional regulation of c-REL by NPD1. The activation of either the canonical/non-canonical NF-κB pathways or c-REL carboxyl-terminal phosphorylation by TBK1/IKKϵ results in accumulation of REL proteins in the nucleus. Depending on the conditions, homo- or heterodimers containing c-REL can form. (1) c-REL promoter ligation eventuates in c-REL protein synthesis, which reinforces the autoregulation loop, (2) by increasing the content of c-REL in the NF-κB dimers, and (3) c-REL-containing dimers bind to the BIRC3 promoter to increase its expression activity, which ensures cell survival. NPD1 augments this auto-regulation loop by shifting the balance toward c-REL homodimers to intensify the expression of both BIRC3 and c-REL genes with subsequent protein synthesis. This shift allows for the restoration of cell homeostasis and thus promotes survival. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is depicted for ease of understanding the protein synthesis step in the pathway.
